 So, you just deleted a file from your computer or smartphone. Wondering what happens next? Where does the file go? Can it be recovered? Well, the guide below will answer in detail: where do deleted files go on different operating systems, and what you can do to recover them if they were permanently deleted.
So, you just deleted a file from your computer or smartphone. Wondering what happens next? Where does the file go? Can it be recovered? Well, the guide below will answer in detail: where do deleted files go on different operating systems, and what you can do to recover them if they were permanently deleted.
What Happens When You Delete a File
In most cases, a deleted file will go to the device’s trash where it remains for a specific time period, or until it’s deleted or restored. But, there are exceptions to this and the trash feature works differently, depending on the device you’re using. Most platforms also allow you to delete a file permanently, i.e., bypass the trash.
Here’s an overview of what happens when you delete a file on Windows, macOS, iPhone, and Android:
Windows PC
Windows has a Recycle Bin that stores deleted files until they’re restored, or the Recycle Bin is emptied. If you have Storage Sense enabled, Windows will periodically empty the Recycle Bin.
By default, Windows allocates around 5% of your total storage space to the Recycle Bin. However, this is adjustable using the Recycle Bin Properties menu. Each volume on your internal storage drive will have its dedicated Recycle Bin (a hidden folder called $RECYCLE.BIN), but all deleted files are displayed together in the Recycle Bin app.
Unless it was deleted or disabled, the Recycle Bin can be easily located on your Desktop, or you can search for it in Windows Search.
When a file doesn’t go to the Recycle Bin upon deletion, it’s typically because of the following reasons:
- The Recycle Bin is disabled.
- You deleted the file using the Shift + Delete shortcut.
- The file was too large for the Recycle Bin.
- You deleted the file from a removable drive like a USB drive, or a memory card. External hard drives are an exception here, since most of them have their own Recycle Bin.
Mac Computers
On macOS, deleted files are moved to the Trash, or Bin. These files remain there for 30 days by default. However, if you’ve unchecked the Remove items from the Bin after 30 days option in Finder settings, the deleted files will remain in the Bin indefinitely, until you restore them, or manually empty the Bin.
The macOS Trash is a Special Folder (the folder itself is called .Trashes, and is hidden), and it only takes up space if there are any files in it. There’s no specific allocation of storage space to the folder. Mac automatically creates a .Trashes folder on removable storage drives.
To access the Trash, you can simply click on the trashcan icon on the Dock, or search for it in Spotlight Search (Command + Space).
Unlike Windows, files that were deleted from a removable drive will also be moved to the Trash, unless you permanently deleted them by using the Option + Command + Delete shortcut or the Terminal.
iOS Devices
On iPhone and iPad, deleted files go to the Recently Deleted folder for 30 days, before being removed permanently. This applies to files deleted using the Files app, whether stored on iCloud, or the device’s local storage. Keep in mind, files deleted from iCloud will be deleted across all your devices.
Deleted photos and videos can be found in the Recently Deleted album in the Photos app.
The Recently Deleted folder will take up space on your storage device, and the iCloud Drive, depending on the files’ original location–local storage, or iCloud.
To view and manage the Recently Deleted folder, open the Files app > Browse > Recently Deleted.
If you wish to delete any files permanently, you’ll need to manually empty the Recently Deleted folder using the Files app.
Android Devices
Where do deleted files go when deleted on an Android device? Well, Android doesn’t have a dedicated trash folder to temporarily store deleted files. The primary reason for this is the small storage space in Android devices, usually hovering around the 32 GB mark. Having a dedicated bin or trash folder that consumes the already limited storage space is not feasible.
However, the photos, file manager, and email apps for your specific smartphone may have their own trash folder. You can access these folders using the specific app.
Is It Possible to Recover Deleted Files?
Yes. It’s possible to recover deleted files, even if they were deleted from the Recycle Bin and Trash, or they were deleted permanently right from the get-go. How is this possible? Well, when a file is deleted, it’s not actually wiped out from the storage drive. The specific data block it occupied is marked as available for use, which means the file is technically still there until a new file overwrites it. In essence, the file is simply made invisible to the operating system.
There are data recovery programs that can find and recover these deleted files. However, there are some factors that will affect the success of the data recovery scan:
- ⏳ Time elapsed since data loss: The sooner you attempt data recovery, the better. As time passes, the OS creates configuration and system files that take up unused space on your drive and can potentially overwrite the deleted files. We recommend not using the device until it’s time to perform data recovery.
- 📂 Files written to the drive: If you write new data to the drive, data recovery chances may decrease, since the new files can overwrite the data you wish to recover. The only way to be sure of this is to perform a data recovery scan.
- 🔨 Physical damage: Data recovery from a physically damaged storage drive is quite difficult, and we don’t recommend using DIY methods for it. It’s because the drive first needs to be restored to a usable state, before data recovery is attempted, which lies outside the expertise of the average user. Additionally, continued usage of a physically damaged drive can further exacerbate the data loss.
- 🎰 Data recovery attempts: Data recovery scans are stressful to the drive, as each sector is scanned for missing data. Typically, the first data recovery scan is the most successful, and we recommend you use a good data recovery program right away.
- 📱 Device type: Data recovery is fairly straightforward on Windows and macOS. However, it’s complicated on Android devices because you may need to root the smartphone/tablet. The most complex out of the lot are iOS devices–iPhones and iPads.
Note: Data recovery from SSDs is tricky due to a feature called TRIM, which automatically clears up unused data blocks at regular intervals. Once the TRIM command has been run, it’s nigh impossible to get back your data. Therefore, we recommend you perform data recovery as soon as possible if your PC is running an SSD.
How to Recover Deleted Files From Any Device
There are innumerable data recovery programs on the web that claim to recover data from a range of devices. However, you should choose one that has a good track record and is easy to use.
For our data recovery tutorial, we opted to use Disk Drill. It checks all the boxes of an excellent data recovery tool–an advanced data recovery algorithm, an easy-to-use GUI, and compatibility with all major file systems, storage device types, and platforms. Disk Drill is available for Windows and macOS. For data recovery from Android and iOS devices, you’ll need Disk Drill for macOS.
The data recovery steps remain the same, regardless of the platform you’re on:
- Download Disk Drill and install it. We recommend you download the program on a separate storage drive and not the one that you wish to scan.
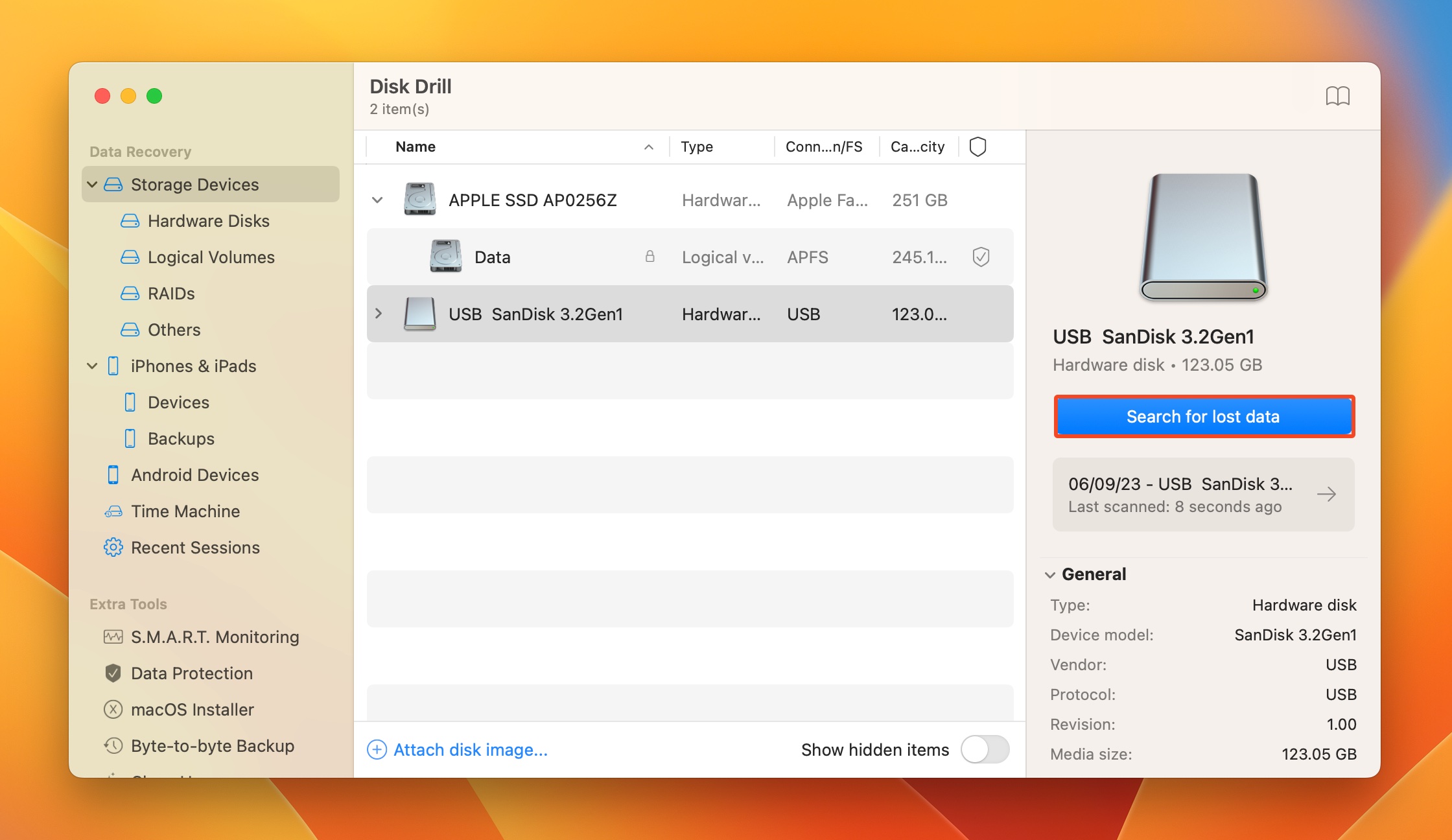
- Open Disk Drill, select the device you wish to scan, and click on Search for lost data.
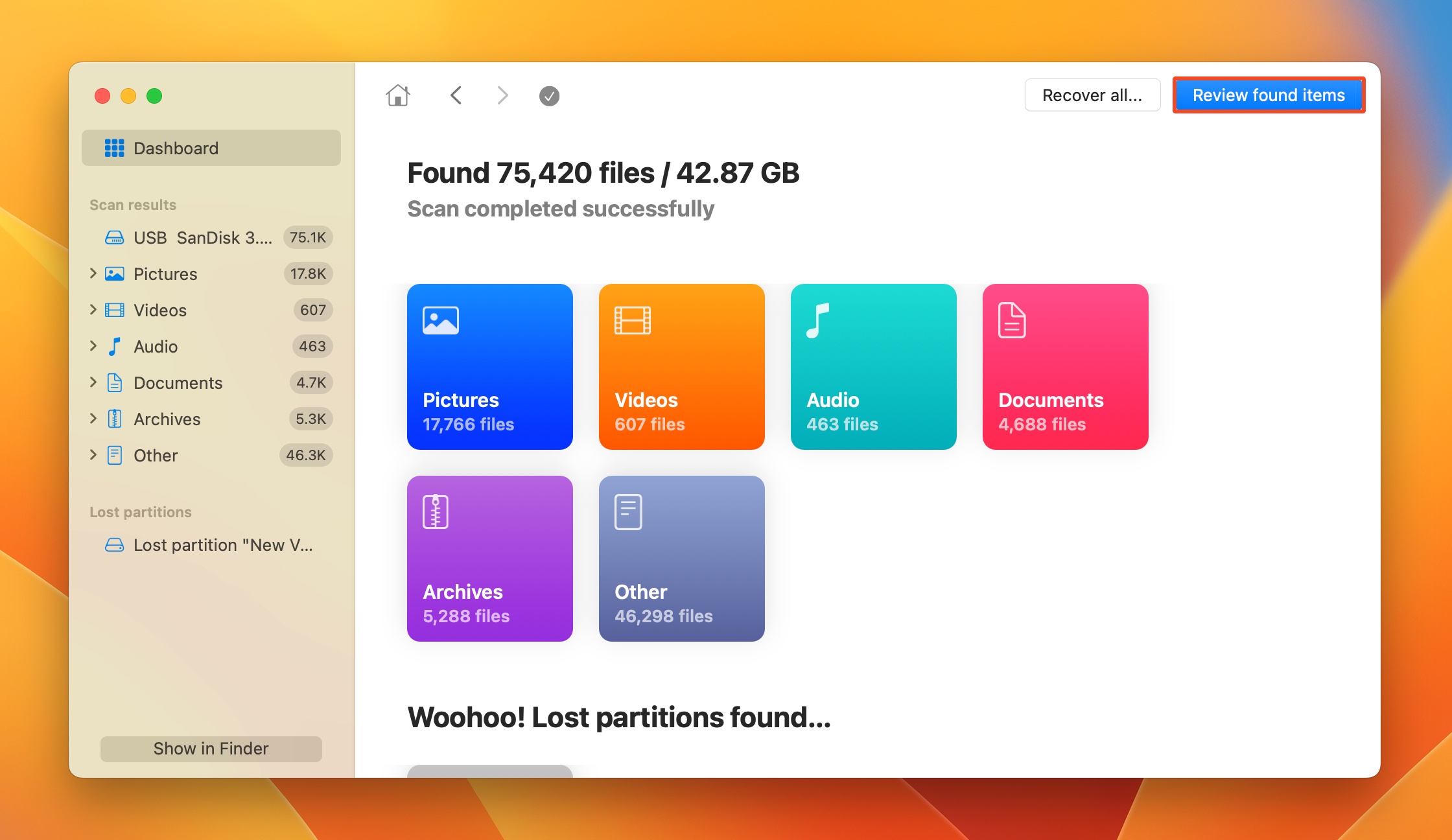
- Click on Review found items to view all recoverable files. To filter out the results, you can click on the relevant file type tile instead (Pictures, Video, Audio, Documents, Archives, and Other).
- Expand the Deleted or lost and Reconstructed sections to view deleted files that can be recovered.
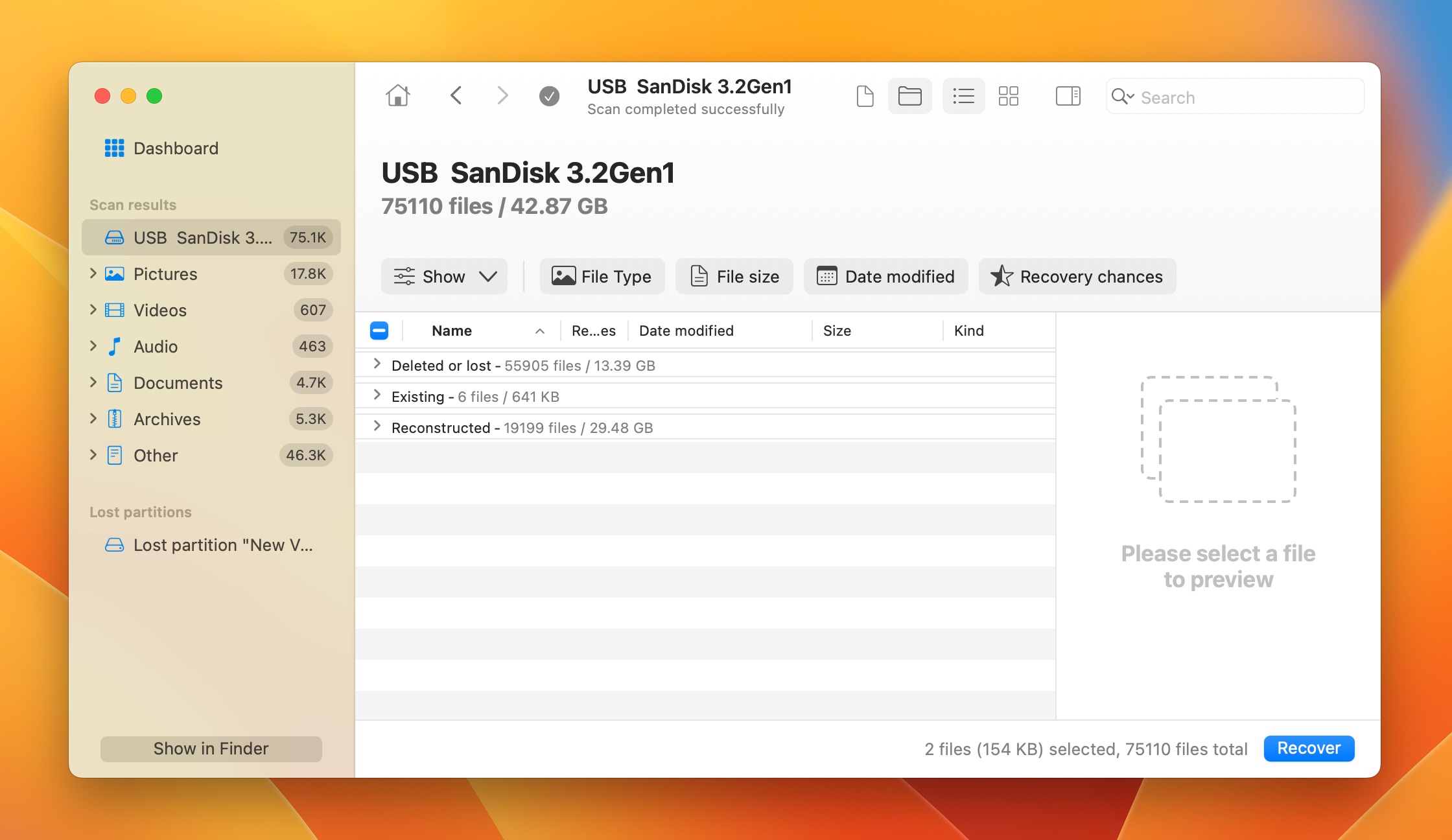
- Use the checkboxes to select the files you wish to recover. Disk Drill’s preview feature may come in handy here–a preview of the currently selected file is displayed automatically, but you can manually preview any file by clicking the eye icon next to its filename. Click on Recover after you’re done selecting the files.
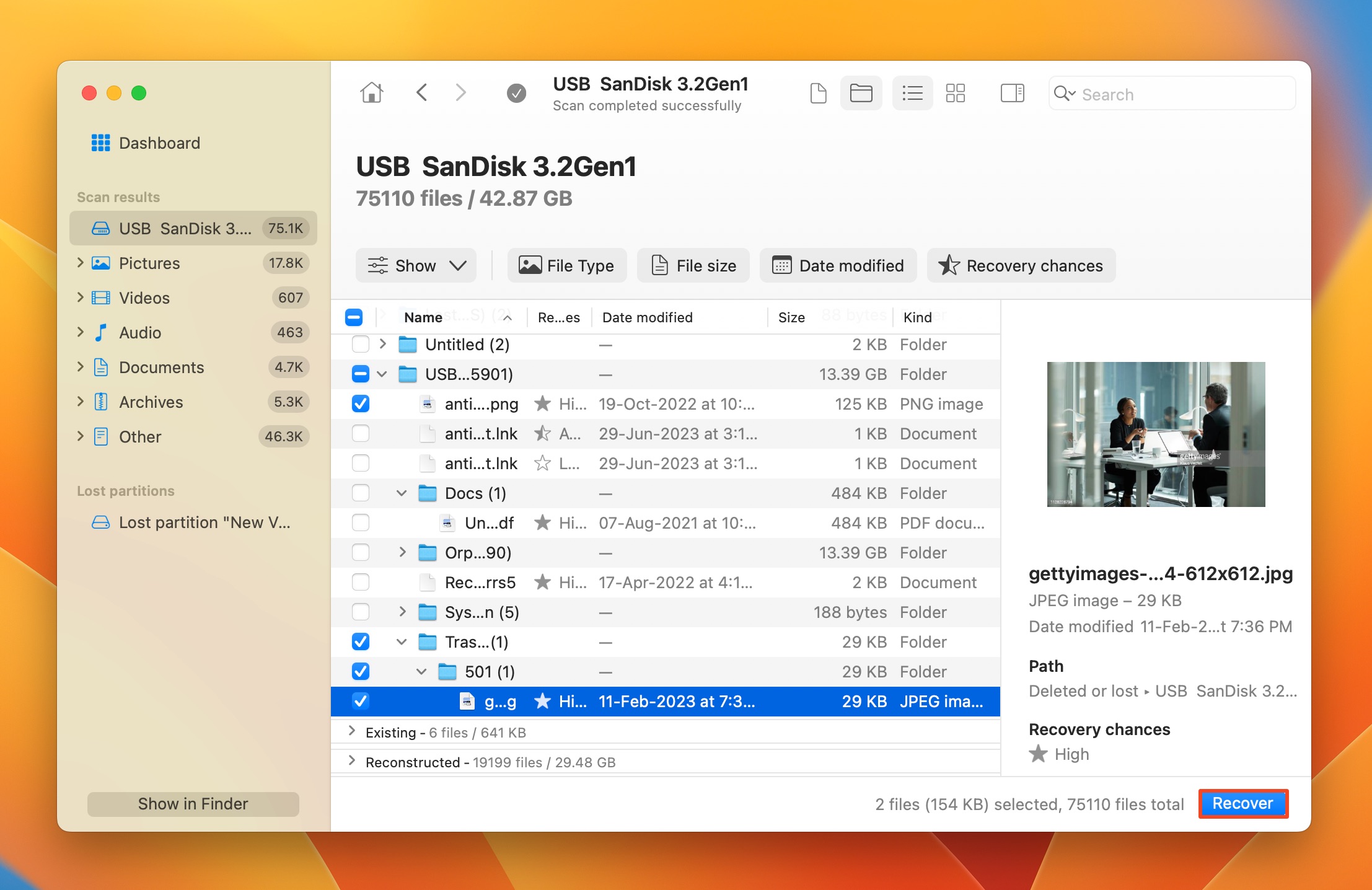
- Choose a recovery destination for the files and click Next. Here too, it’s best to store the files on a different storage drive.
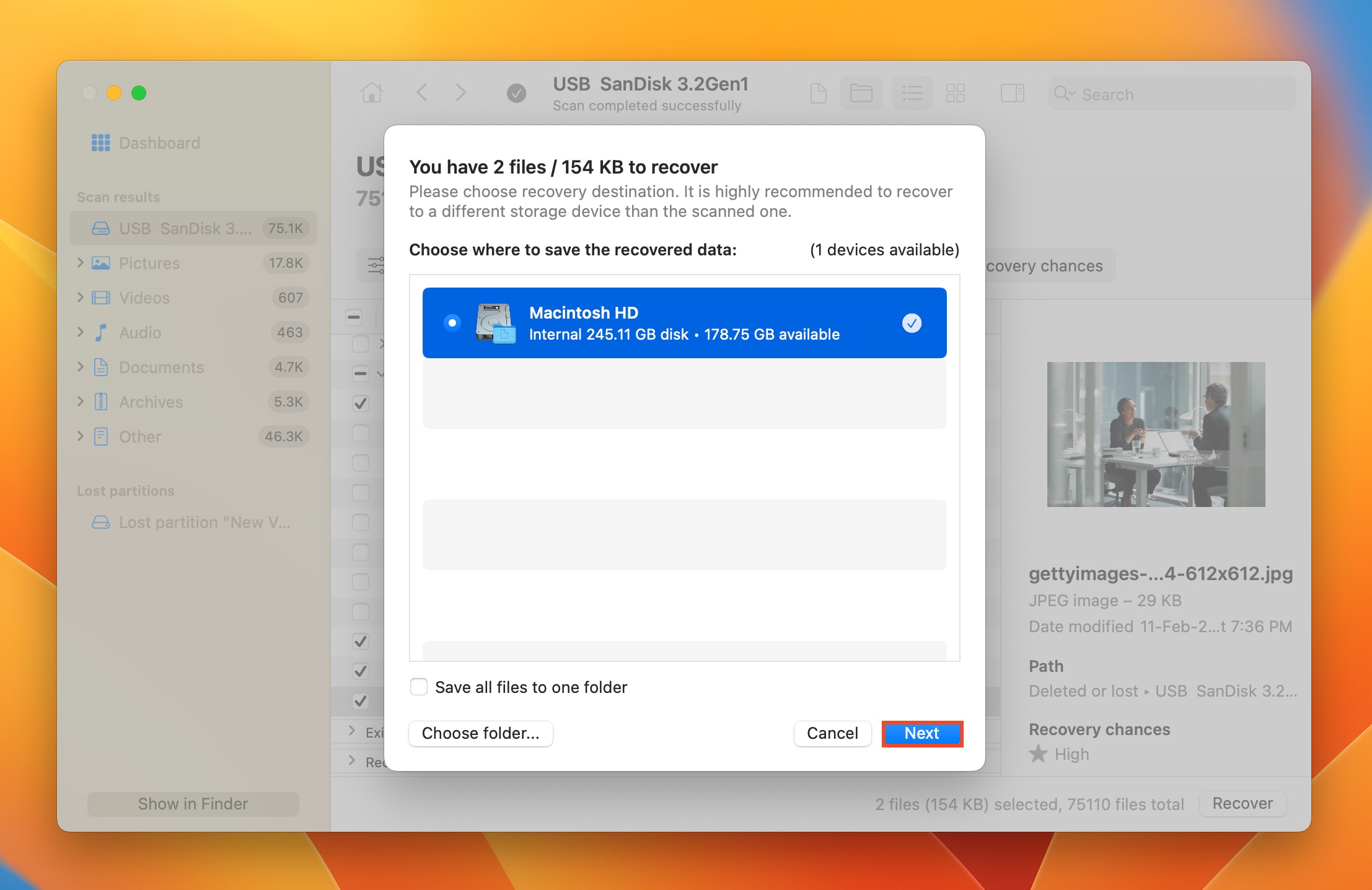
- Disk Drill will recover the selected files.
Note: The Windows version gets a free 500 MB data recovery trial. The Mac version lets you view the recoverable data, but actual recovery requires the Pro version of Disk Drill.
Conclusion
All popular platforms, except Android, have a built-in Recycle Bin or Trash that lets you restore files after they’ve been deleted. So, if you recently deleted a file, it’s likely that it went to your system’s trash folder. Fortunately, even if the files aren’t in the recently deleted folder of your device, they’re still recoverable using a good data recovery program, provided you carefully follow the tips mentioned in the sections above.




