 The folder access denied error can prevent you from reading, writing, or modifying a specific folder. Usually, the issue is not a cause for concern and can be fixed in a few simple steps. Even if there’s a serious issue that caused the error, you will likely retain your data. Use our guide to learn how you can regain access to the folder and secure your files.
The folder access denied error can prevent you from reading, writing, or modifying a specific folder. Usually, the issue is not a cause for concern and can be fixed in a few simple steps. Even if there’s a serious issue that caused the error, you will likely retain your data. Use our guide to learn how you can regain access to the folder and secure your files.
What Causes Folder Access Denied Errors
Folder access denied error messages differ depending on the action you’re trying to perform on the affected folder. If you were copying files to the folder, you’ll usually get the “Destination folder access denied” message. If you attempt to access the folder, without the necessary user rights, Windows will display the “You have been denied permission to access this folder,” or “Folder Access Denied” message.
Regardless of the actual error message, the root cause of the error is insufficient permission to access the folder. You’re more likely to face the folder access denied error on computers that have multiple users with different rights.
In rare cases, the error could crop up due to bad sectors on the hard drive, or a problematic Windows update.
How to Fix Folder Access Denied Error
Fixing the folder access denied error boils down to checking and changing the permission settings for the folder. It could be as simple as switching to an admin account or altering the permission settings. If that doesn’t resolve the issue, it’s likely the storage drive is logically damaged.
Method 1: Use Data Recovery Software
Securing your files should be a priority because the folder access denied error can be the result of logical issues on your drive, or you may not have enough time to go through the fixes and see which one works. Here, third-party data recovery programs are a godsend.
There’s an abundance of data recovery programs, but we chose to go with Disk Drill in this tutorial. The tool is user-friendly, has an advanced data recovery algorithm, and supports all major file systems and storage device types (internal and external HDDs, USB drives, SSDs, SD cards) – all you need to successfully get back your files. Windows users can take advantage of Disk Drill’s free trial, which lets you recover up to 500 MB of data at no cost.
Here’s how to use Disk Drill and get back files from a folder that shows access denied:
- Download Disk Drill and install it.
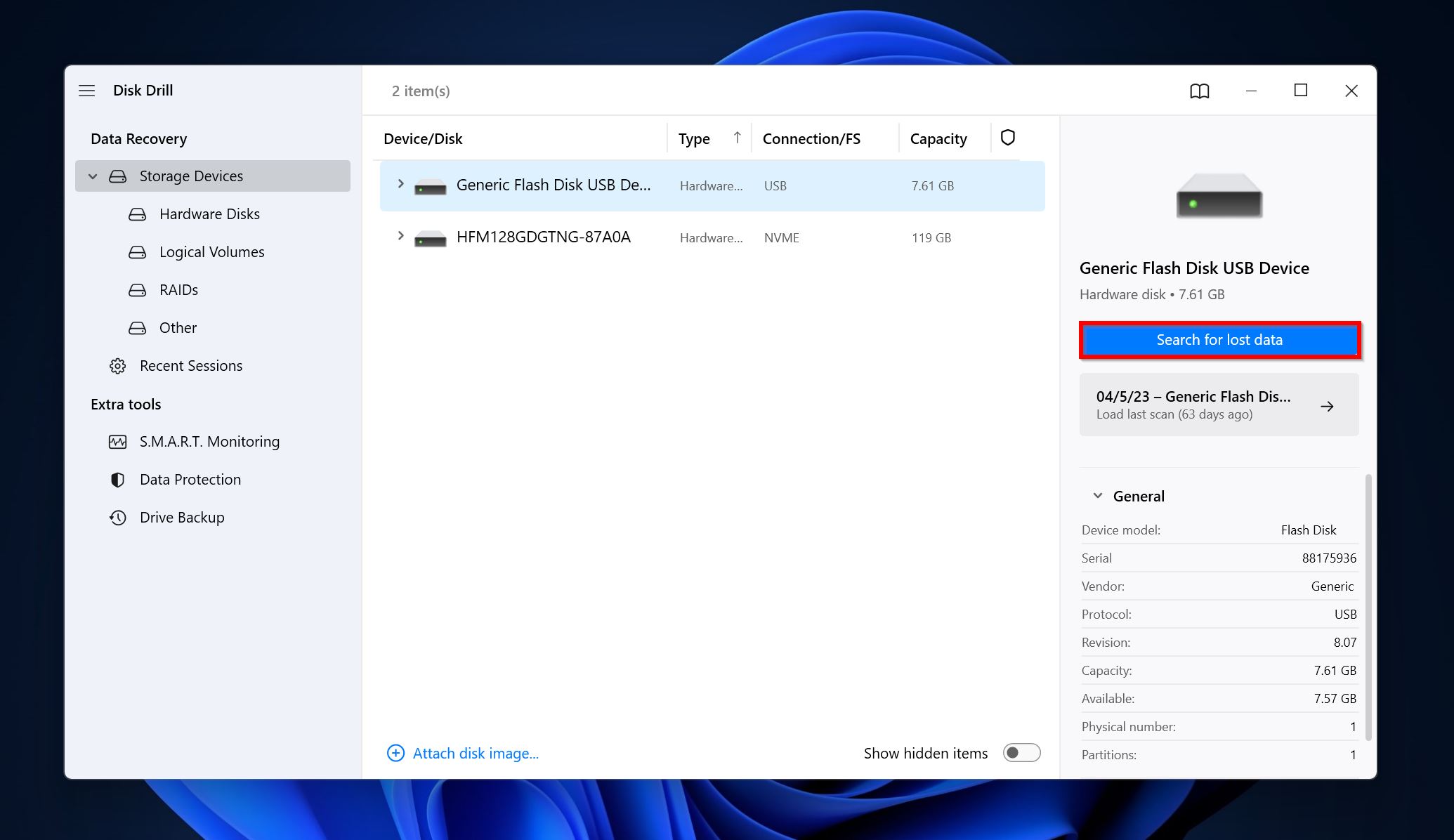
- Open Disk Drill, select the drive which contains the access denied folder, and click on Search for lost data.
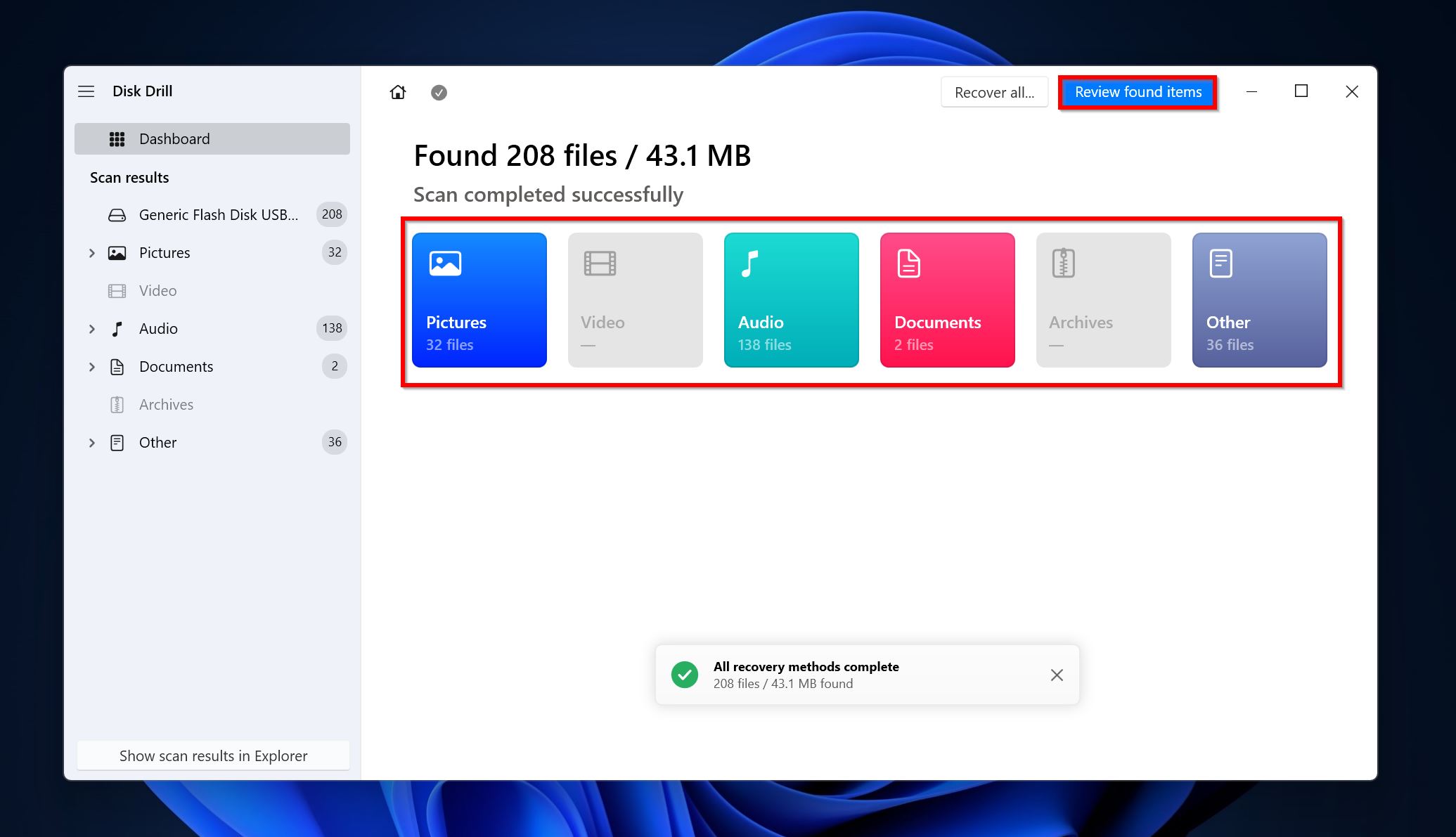
- Click on Review found items to view the recoverable files. You can opt to directly filter out the results by clicking on the relevant file type on this screen as well (Pictures, Video, Audio, Documents, Archives, and Other).
 Expand the Existing section to see the currently stored folders on the disk.
Expand the Existing section to see the currently stored folders on the disk.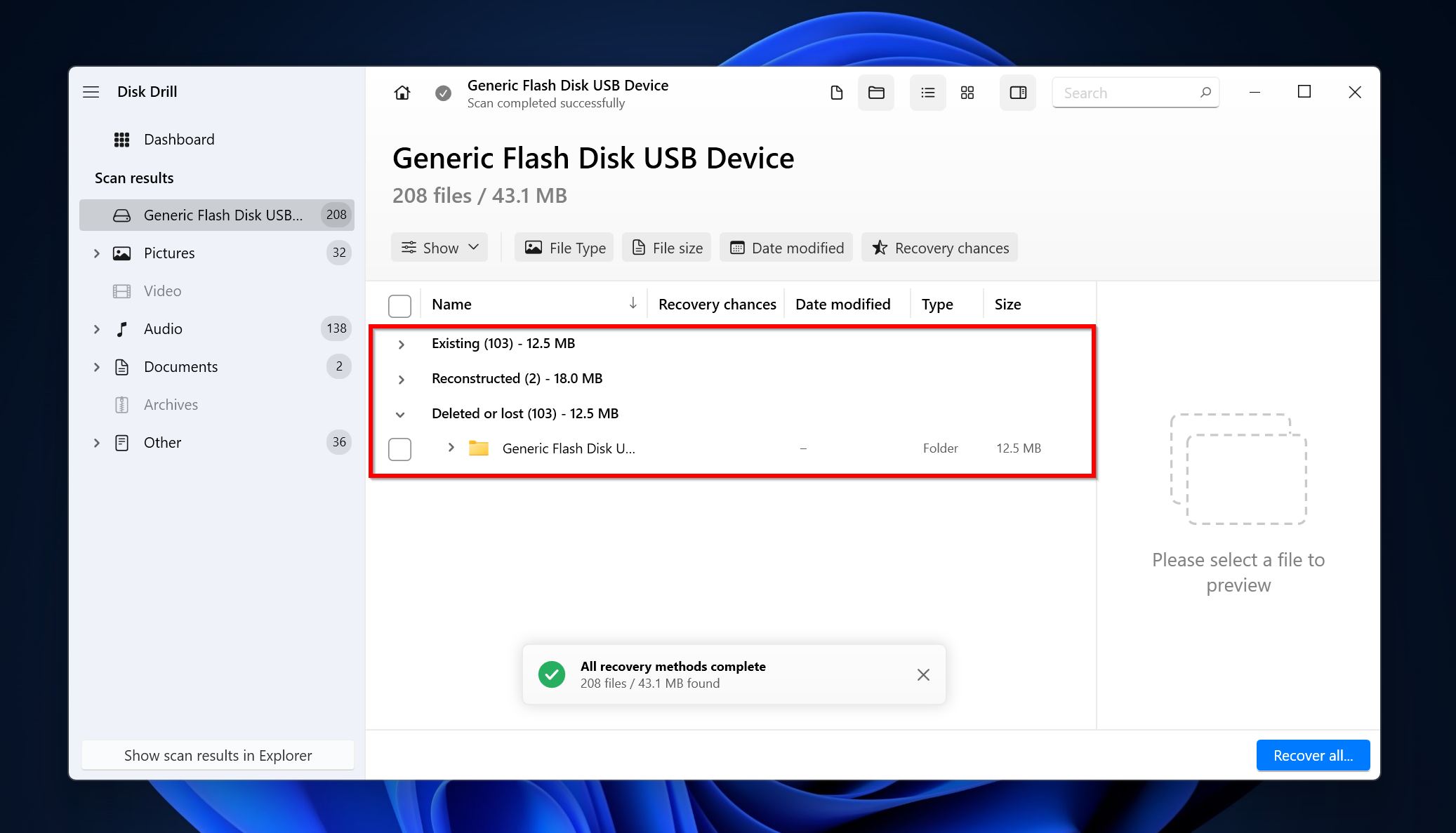
- Use the checkboxes to select the files you wish to recover. Disk Drill displays a preview of the currently selected file, but you can use the eye icon next to the filename to manually preview it. Click on Recover once your selection is complete.
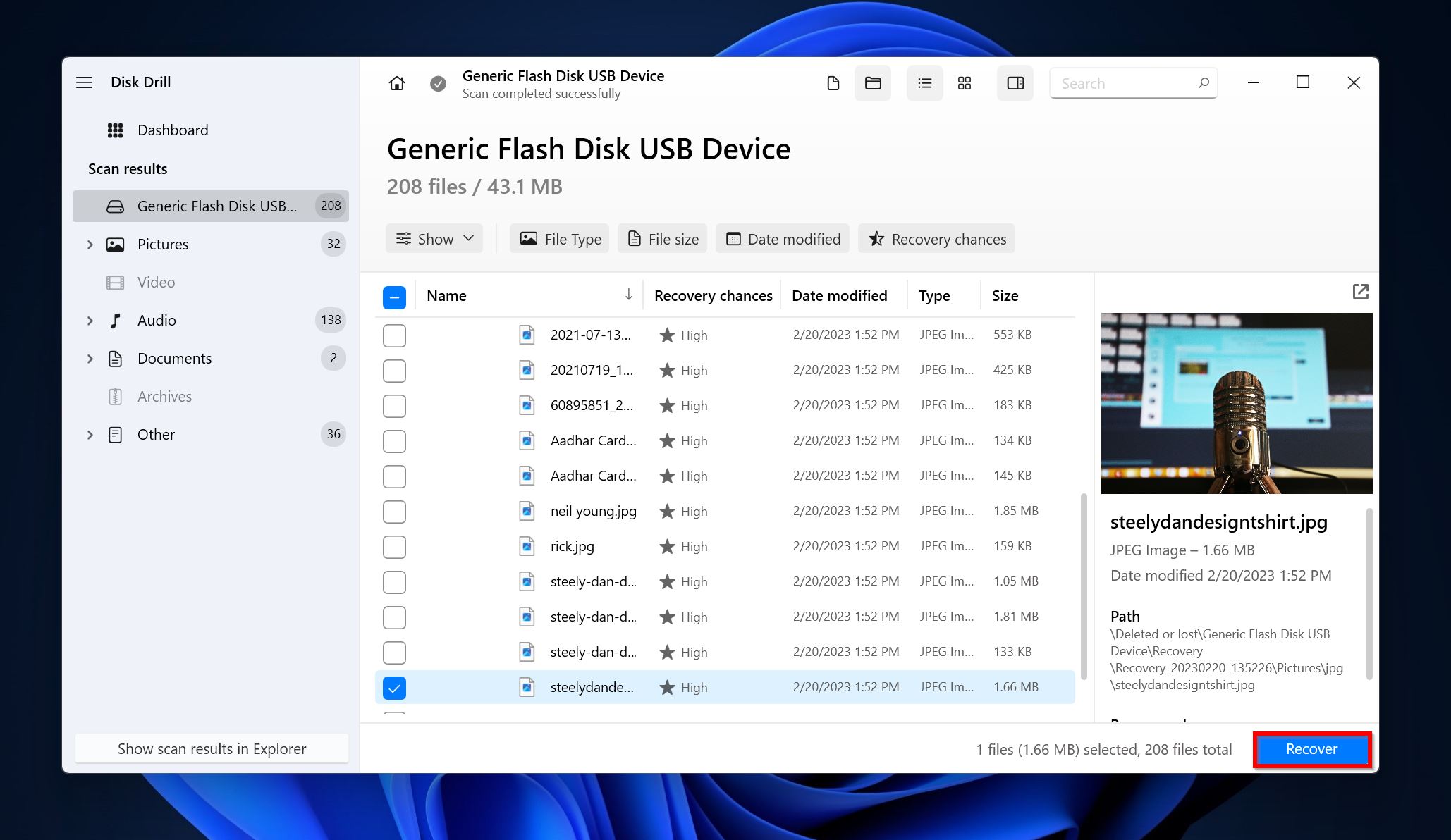
- Choose a recovery destination for the files and click Next.
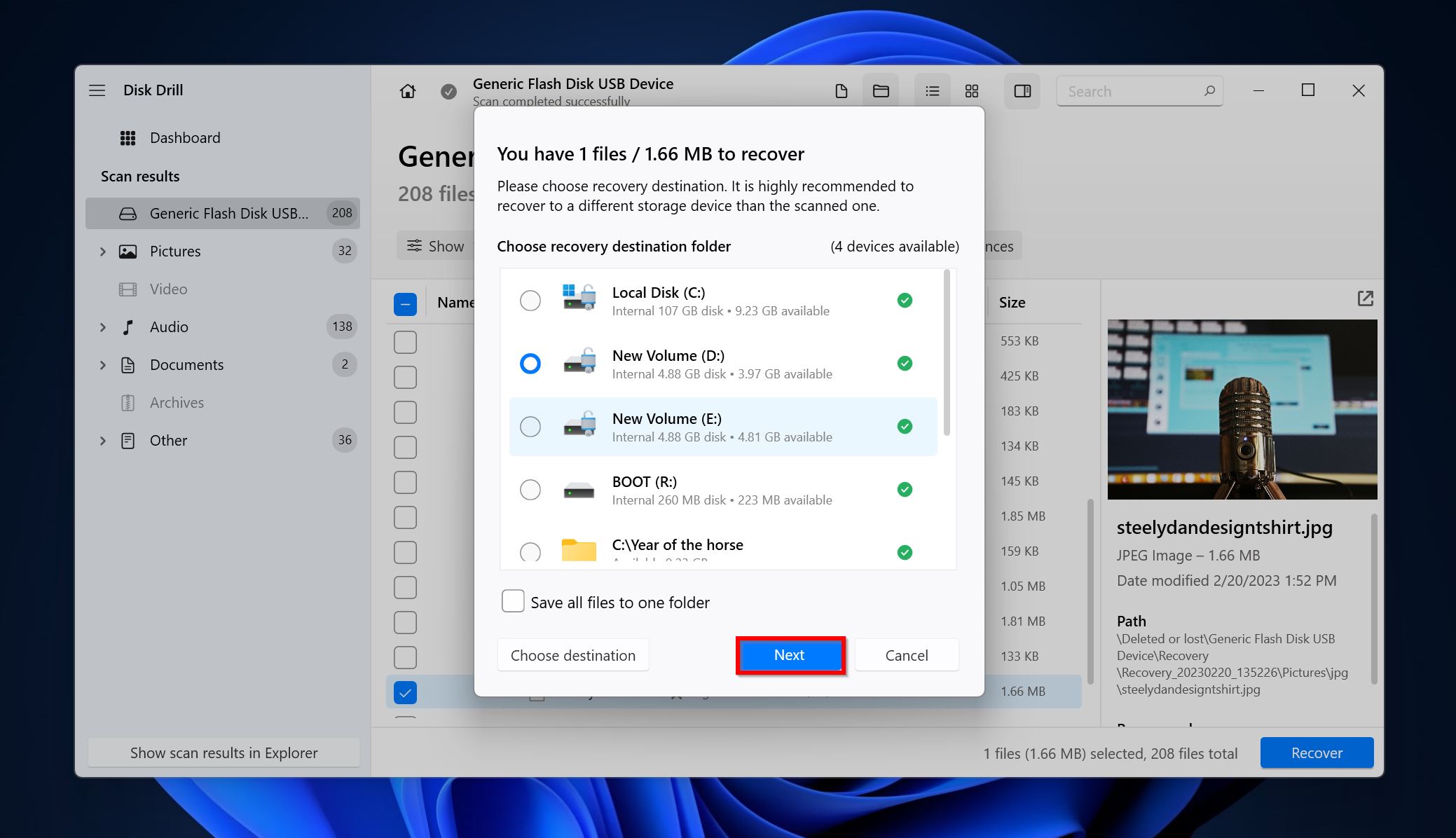
- Disk Drill will recover the selected files.
Method 2: Ensure the Folder Is Not in Use by a Program
The folder access denied error can show up if you attempt to modify or access it while a program is using it in the background. While there’s no way to specifically determine which program could be using the folder, you can use the Task Manager to check for background processes and try to figure out if an app could be using the folder.
Here’s how to use the Task Manager and see what background processes may be running:
- Right-click on the Taskbar and click on Task Manager. You can also press CTRL + SHIFT + ESC to directly launch the Task Manager.
- Go to the Processes tab and check if there’s a background process that could be using the folder you want to access.
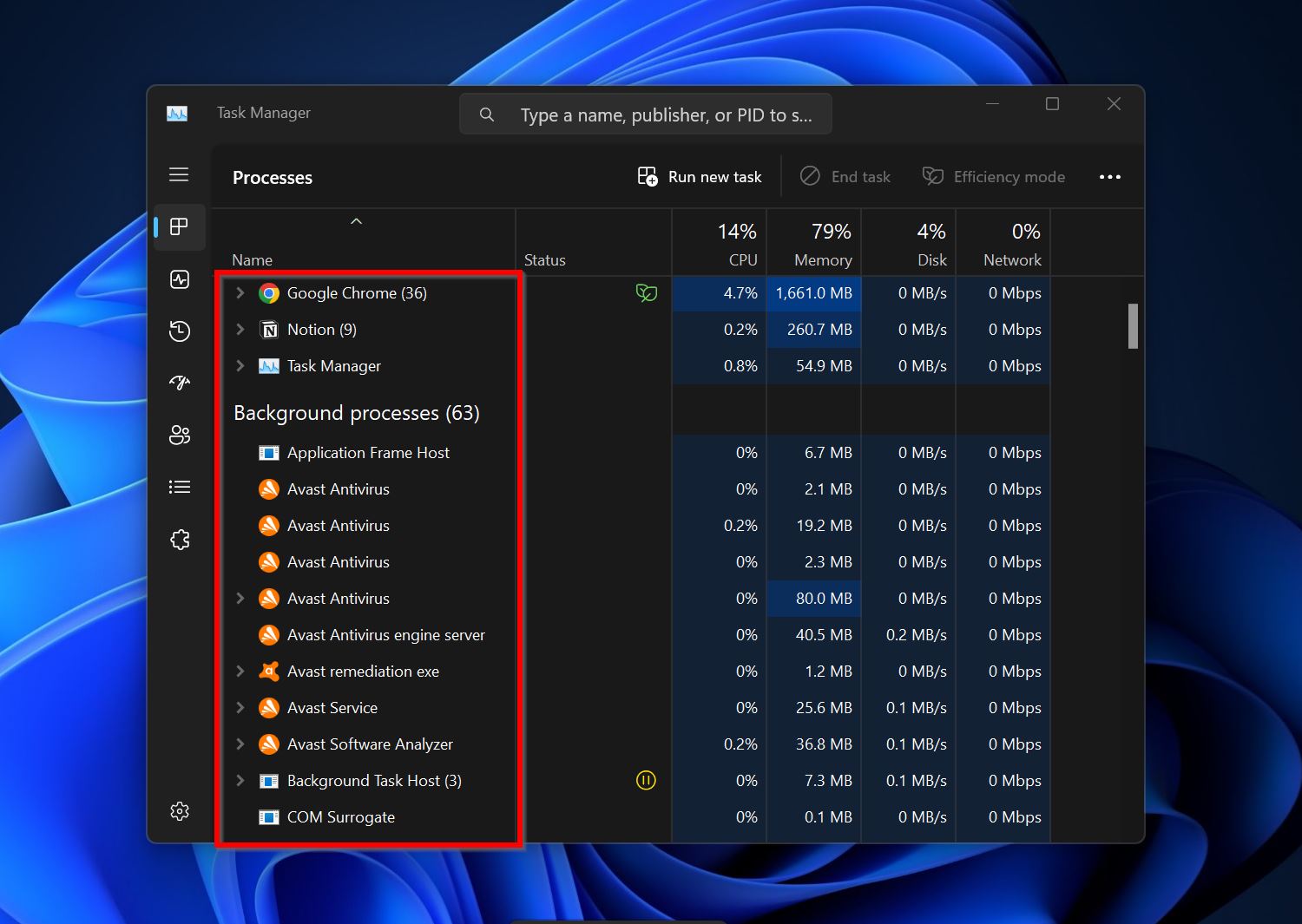
Method 3: Ensure You’re Using an Admin Account
An account with administrative privileges typically has complete access to the folders. If you’re using a regular user account, you may not have enough permissions, which results in the access denied error when accessing certain folders.
To check if the user account you’re logged into is an Administrator, follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start button and choose Settings.
- Click on the Accounts tab.
- Check if there’s an Administrator tag under the profile info, as shown in the screenshot below.
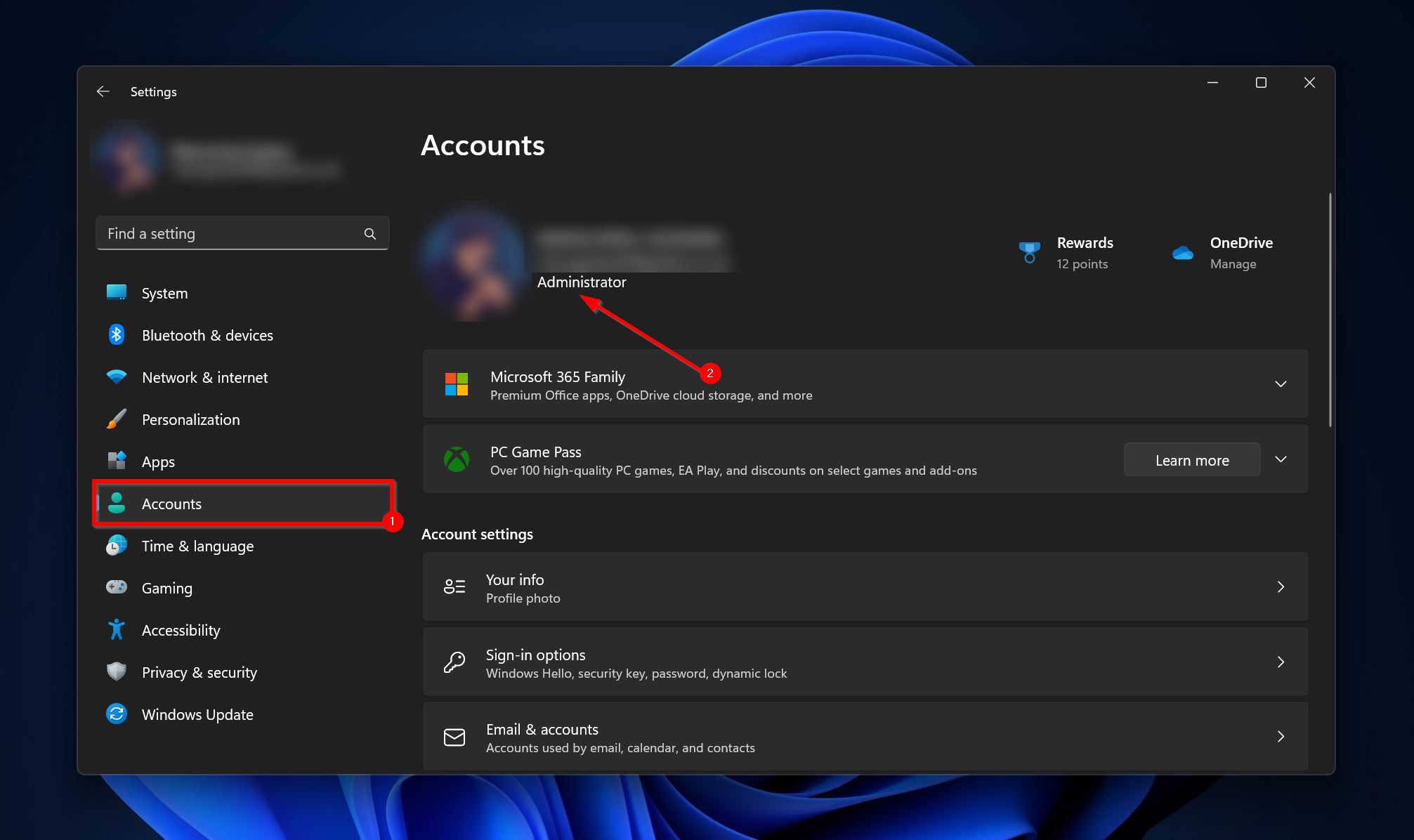
If you’re not logged in as an administrator, switch accounts and log in to one that has the required privileges. You will need it to modify the permission settings in the later methods.
Method 4: Change Folder Ownership
Taking ownership of the affected folder is one of the most effective ways to resolve the folder access denied issue. You can do this using the File Explorer.
Here’s how:
- Open File Explorer (Windows Key + E). Navigate to the folder that you need to access, right-click on it and choose Properties.
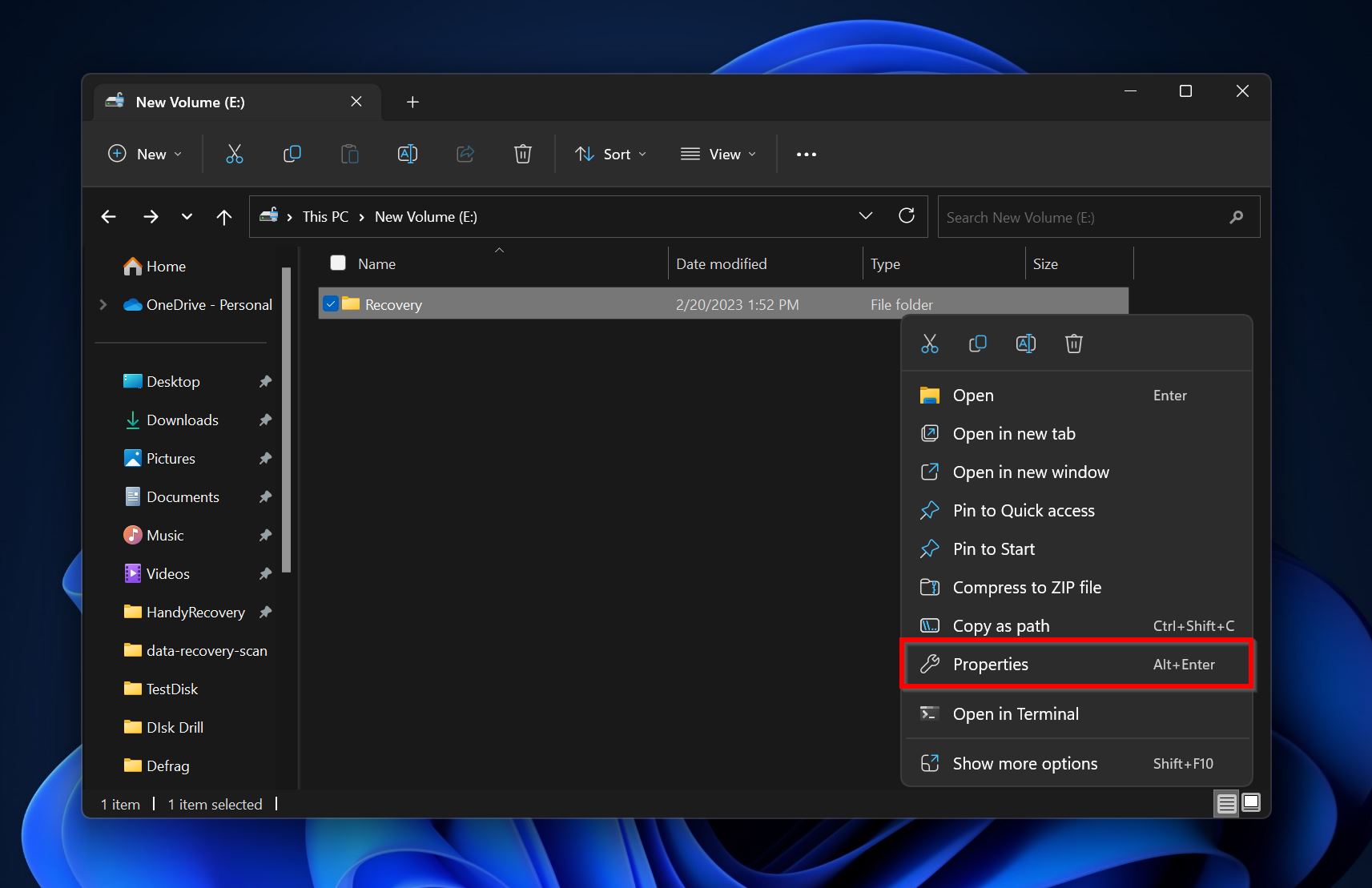
- Click on the Security tab, then select Advanced.
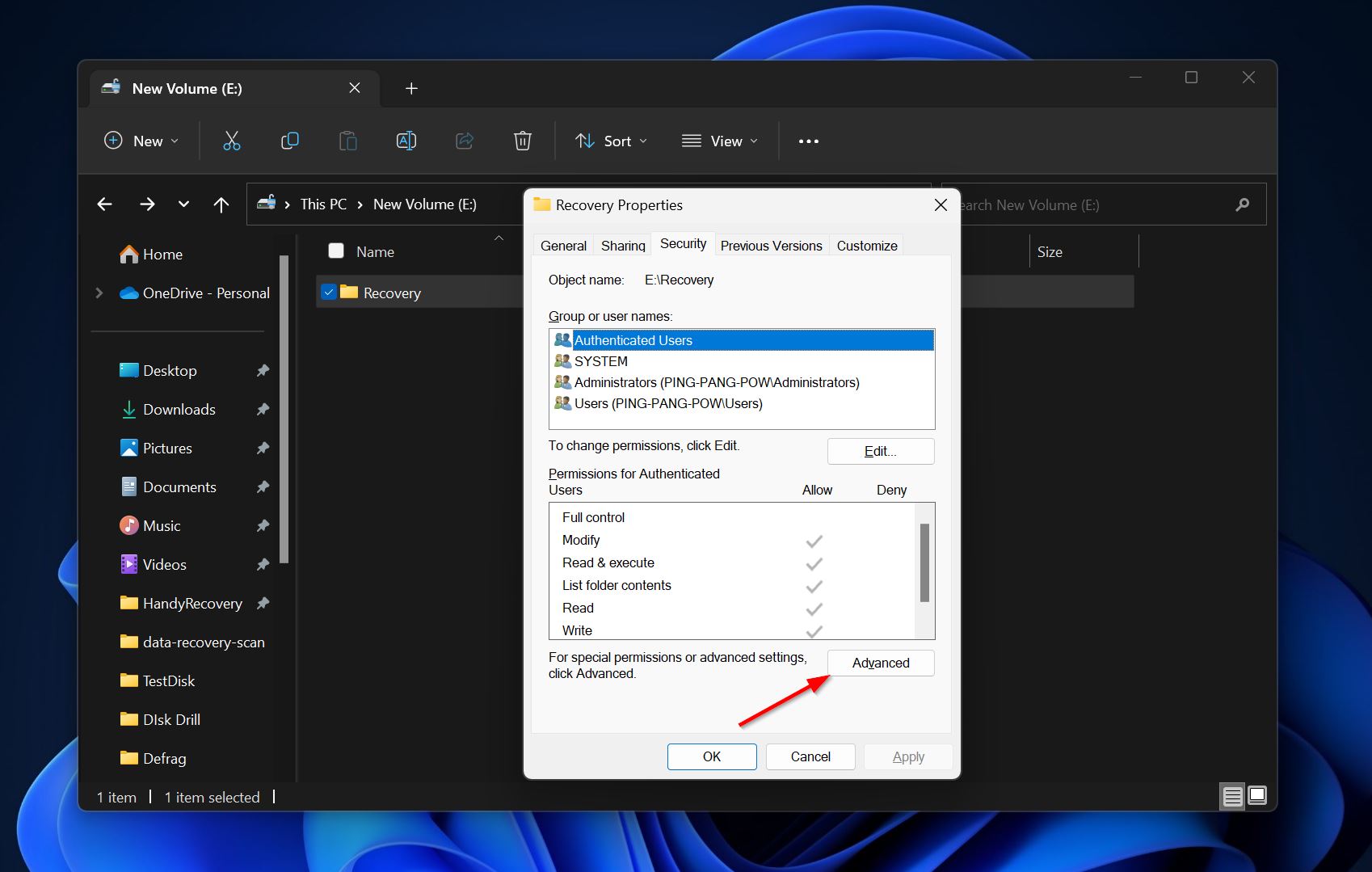
- Click on the Change option next to the Owner field.
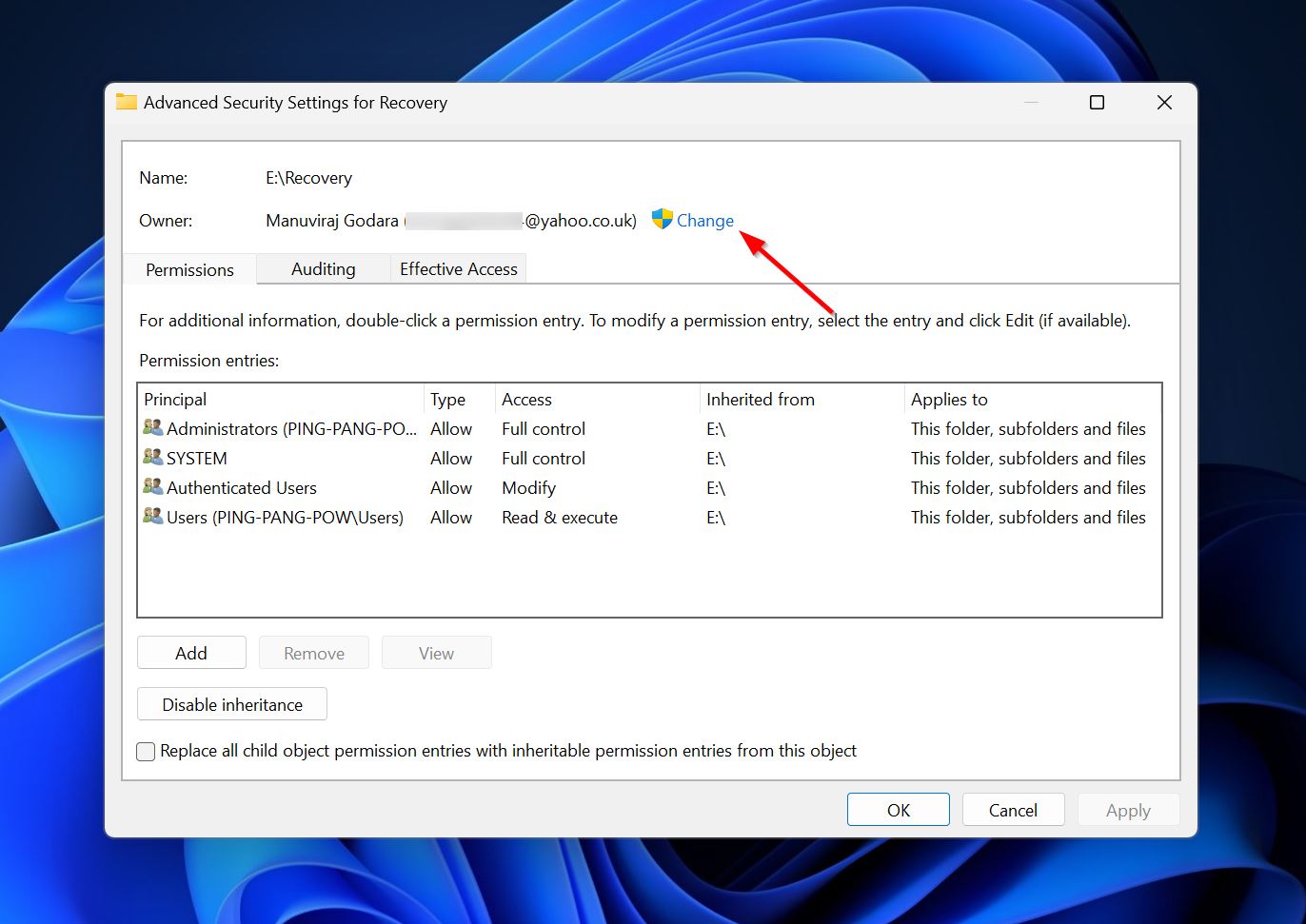
- In the Object name field, type in your user account or the account you wish to assign ownership to, and click Check Names. Click on OK.
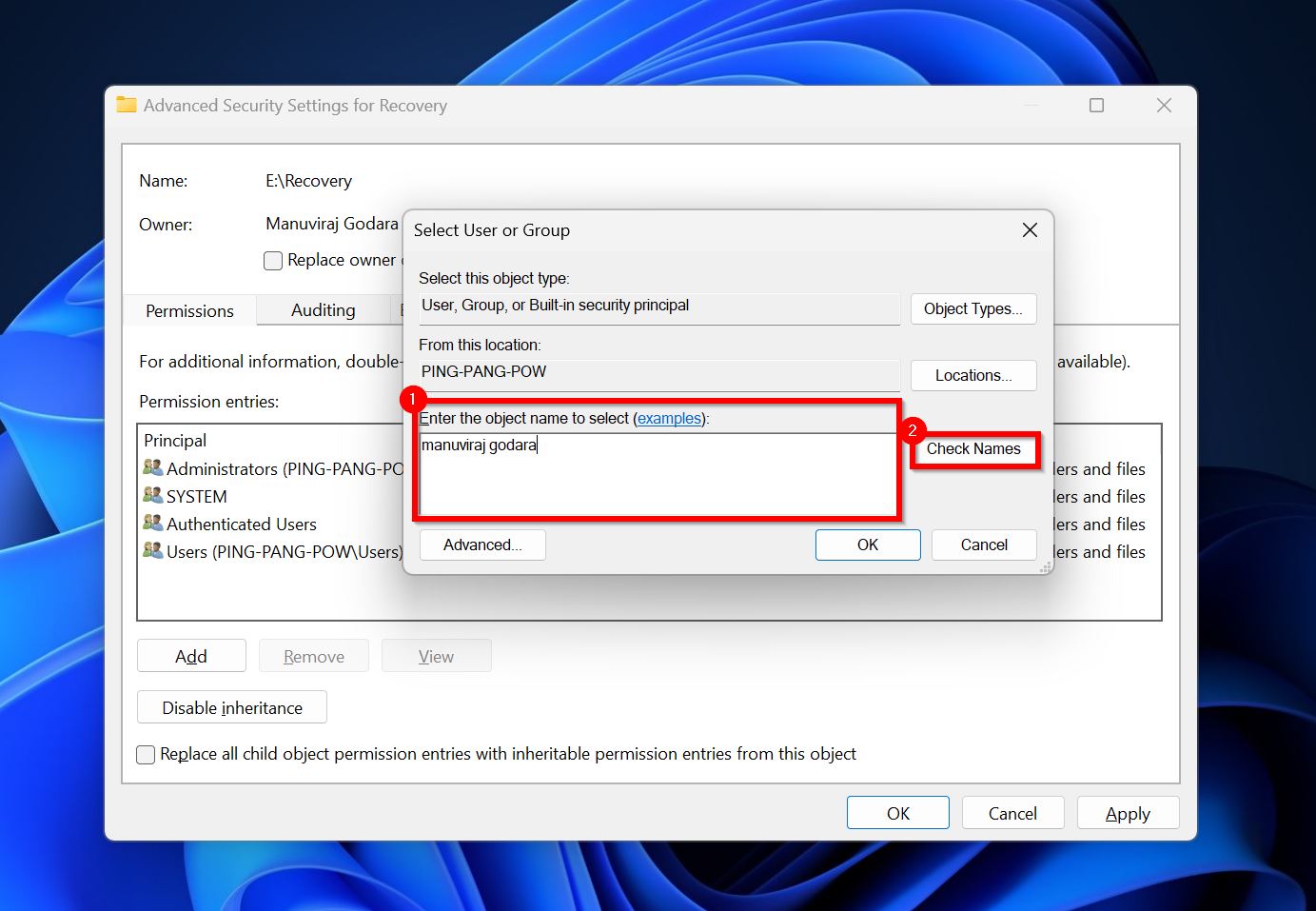
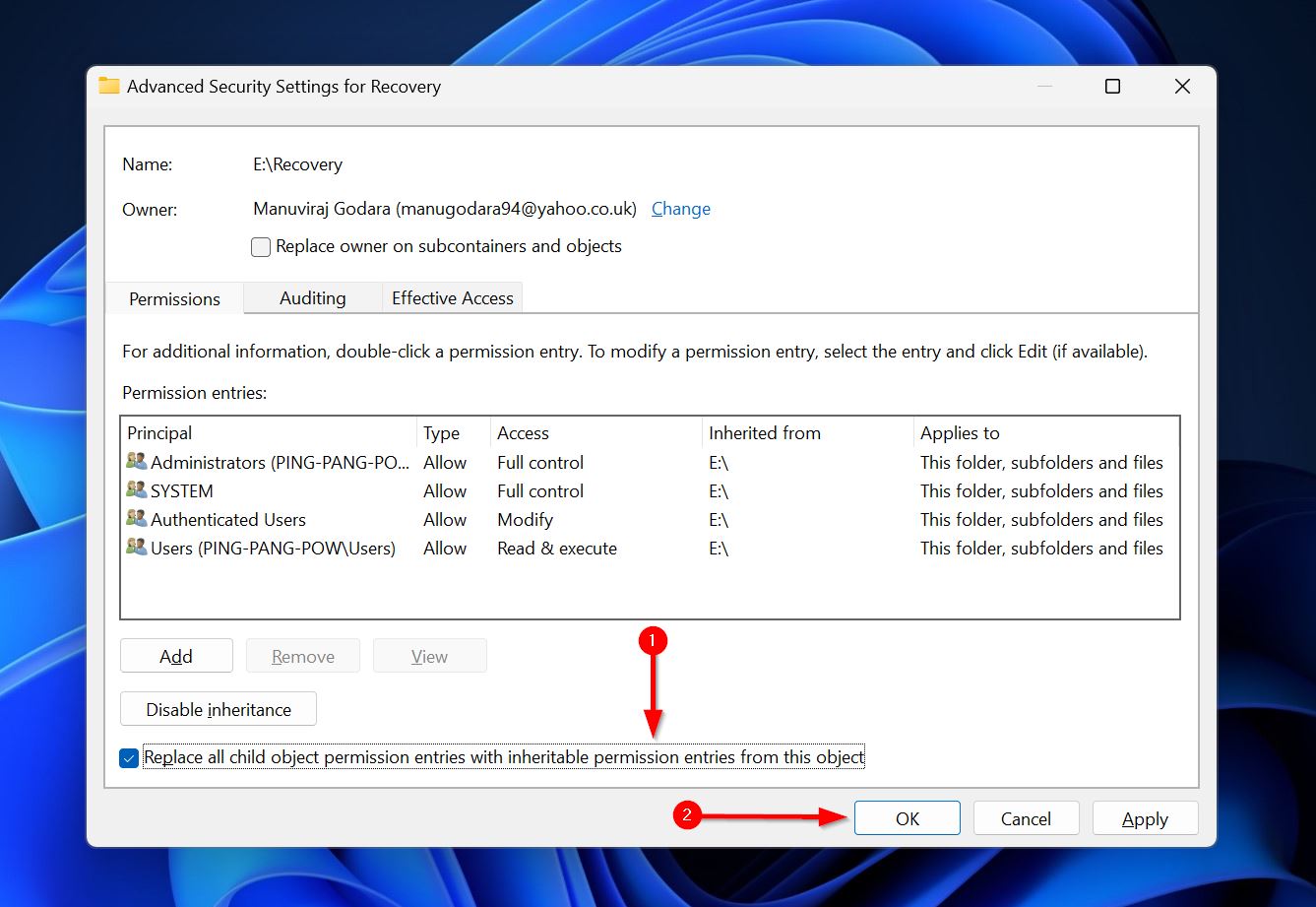
- Check the “Replace all child object permission entries with inheritable permission entries from this object” option and click OK.
Method 5: Change the Folder Permissions
If you’re unable to access the folder after taking ownership of the folder, it’s a good idea to review the folder permissions and see the extent of control different users have over the folder.
To check the folder permissions, follow these steps:
- Open File Explorer (Windows Key + E), right-click on the folder and click Properties.
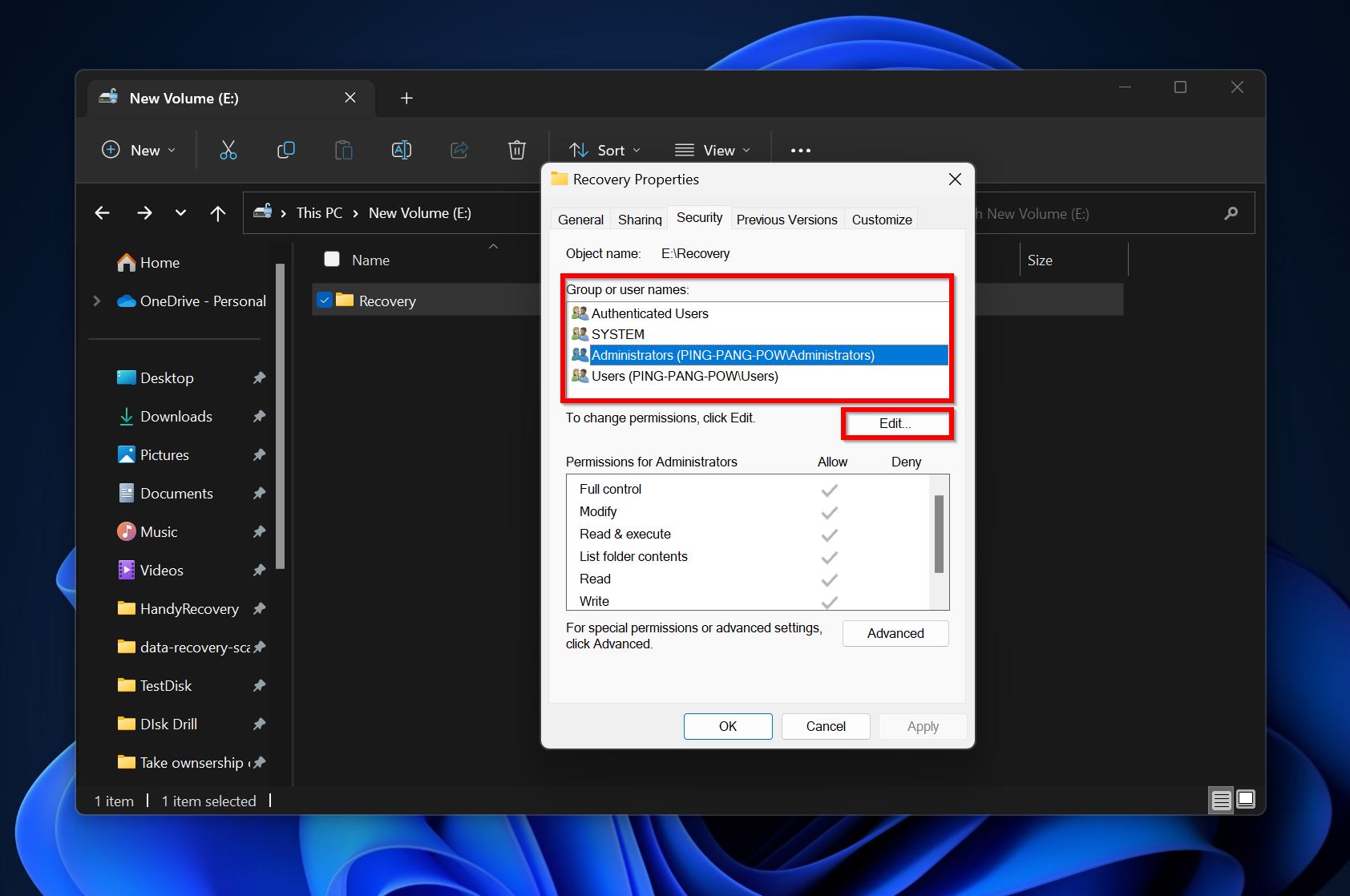
- Again, visit the Security tab. In the Group or user names field, select the user you wish to edit the permissions for, and click on Edit.
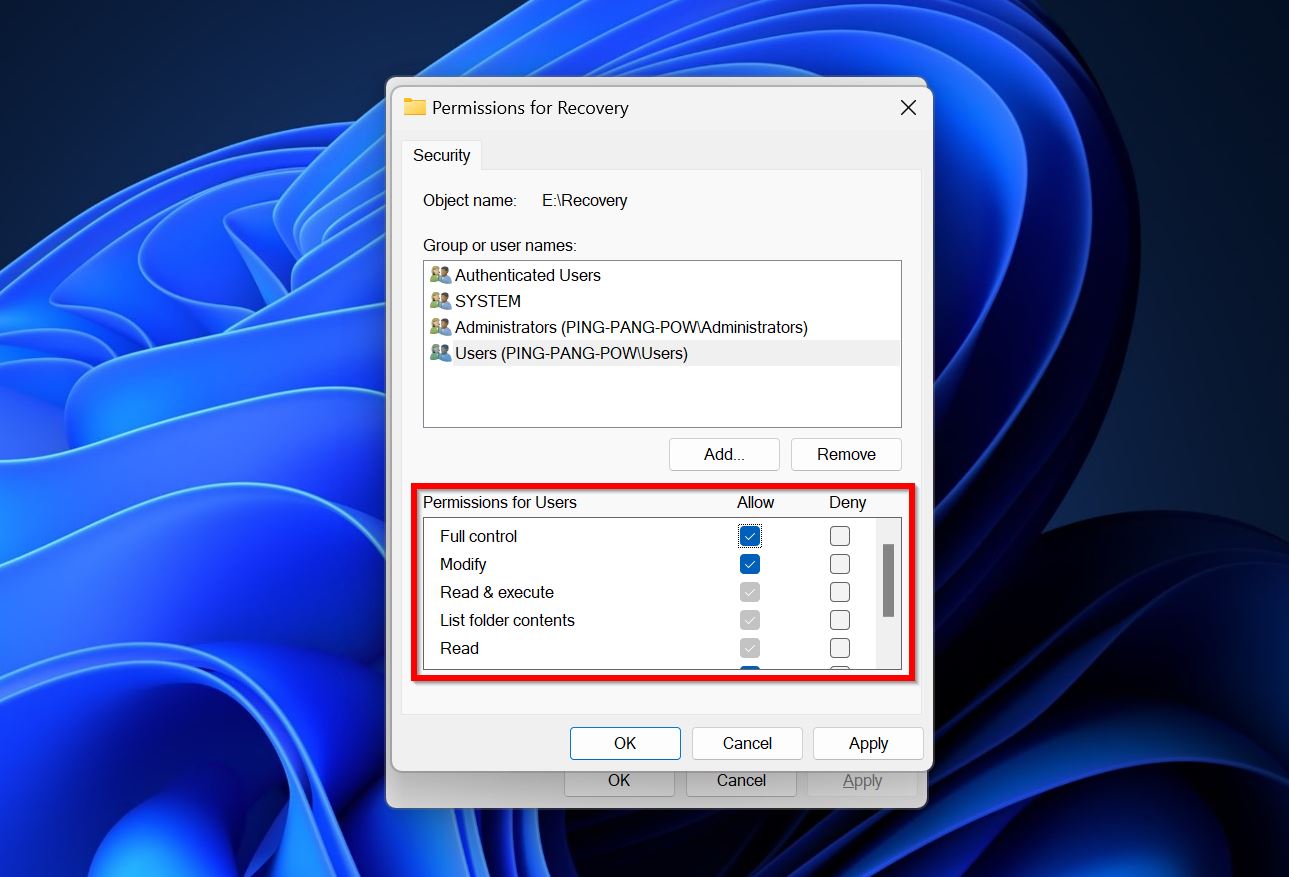
- In the Permissions for users section, check the permissions you wish to enable under the Allow column. If you trust the user account, it’s best to check the Full control option. Click on OK.
Method 6: Check the Antivirus Settings
If your antivirus suspects there’s a malicious file stored in the folder in question, it may restrict access to it. After ensuring that you have the required permissions for the folder, it’s a good idea to check your antivirus program’s settings.
If you’re sure the folder doesn’t contain any malware, open your antivirus program’s settings. Disable any folder shield and ransomware protection options and see if you can access the folder. If that doesn’t work, disable the antivirus program and check if you’ve regained access to the folder.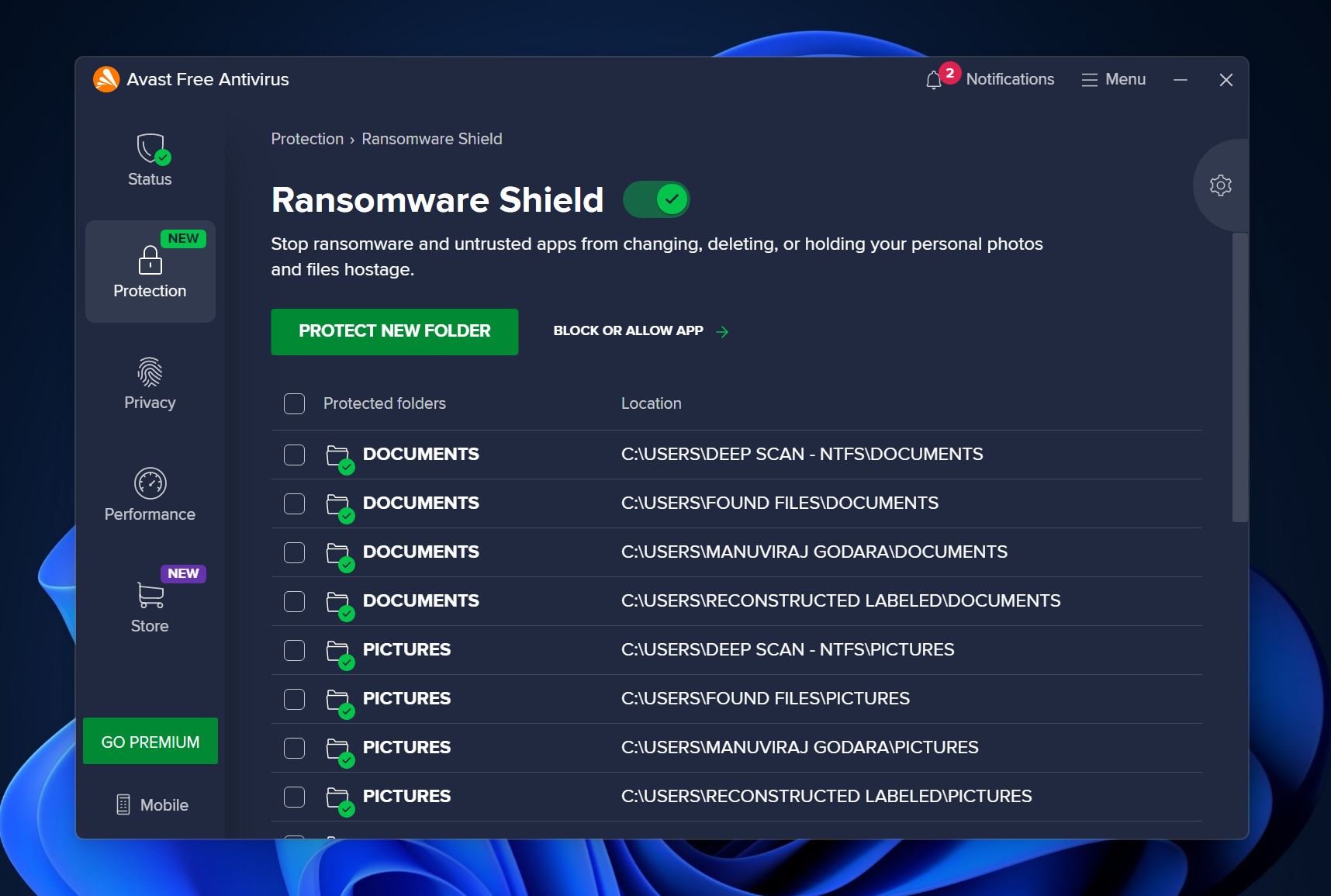
If you can access the folder after disabling your antivirus, add the folder as an exception in the antivirus settings and enable the antivirus program.
Method 7: Turn on Network Discovery & File Sharing
If the folder you’re unable to access is stored on a network location, it’s recommended you check if Network discovery and file sharing is turned on. If the option is switched off, Windows will display the “Destination folder access denied” message when you try to copy files to or from the network location.
To switch on Network discovery and file sharing, follow these steps:
- Type “control panel” in Windows Search (Windows Key + S) and click on the Control Panel.
- Click on the Network and Internet option.
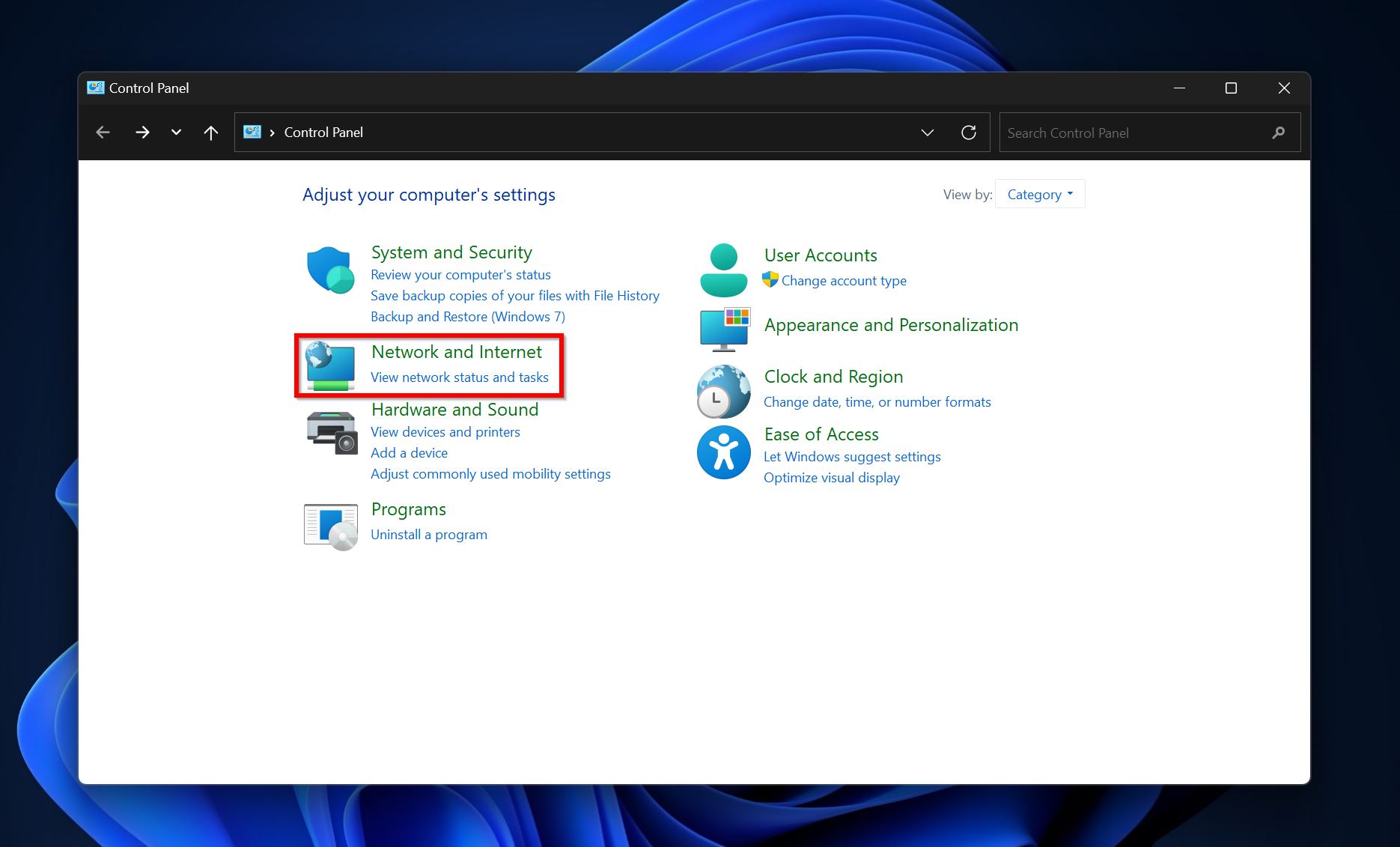
- Click on the Network and sharing center option.
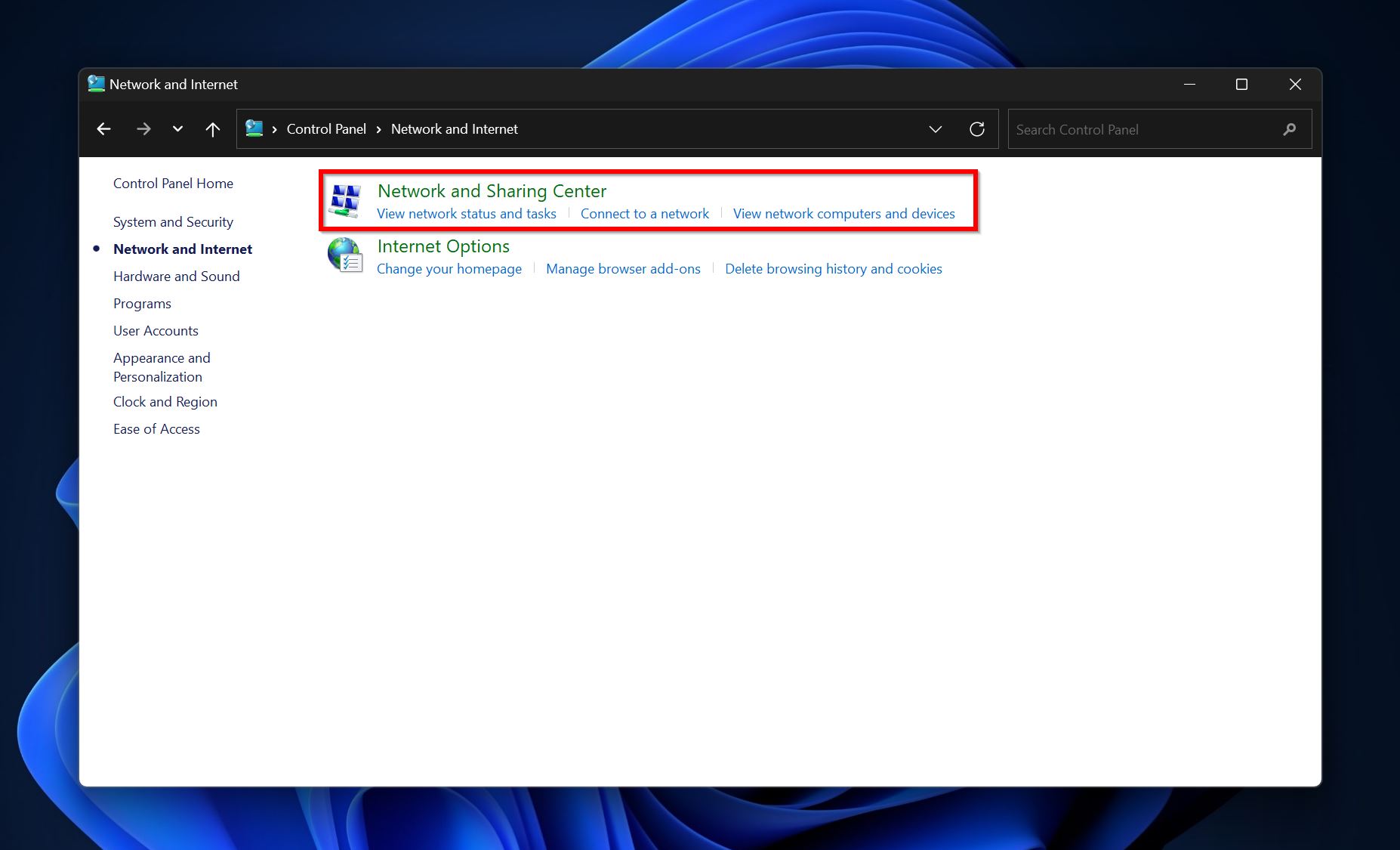
- Here, click on Changed advanced sharing settings.
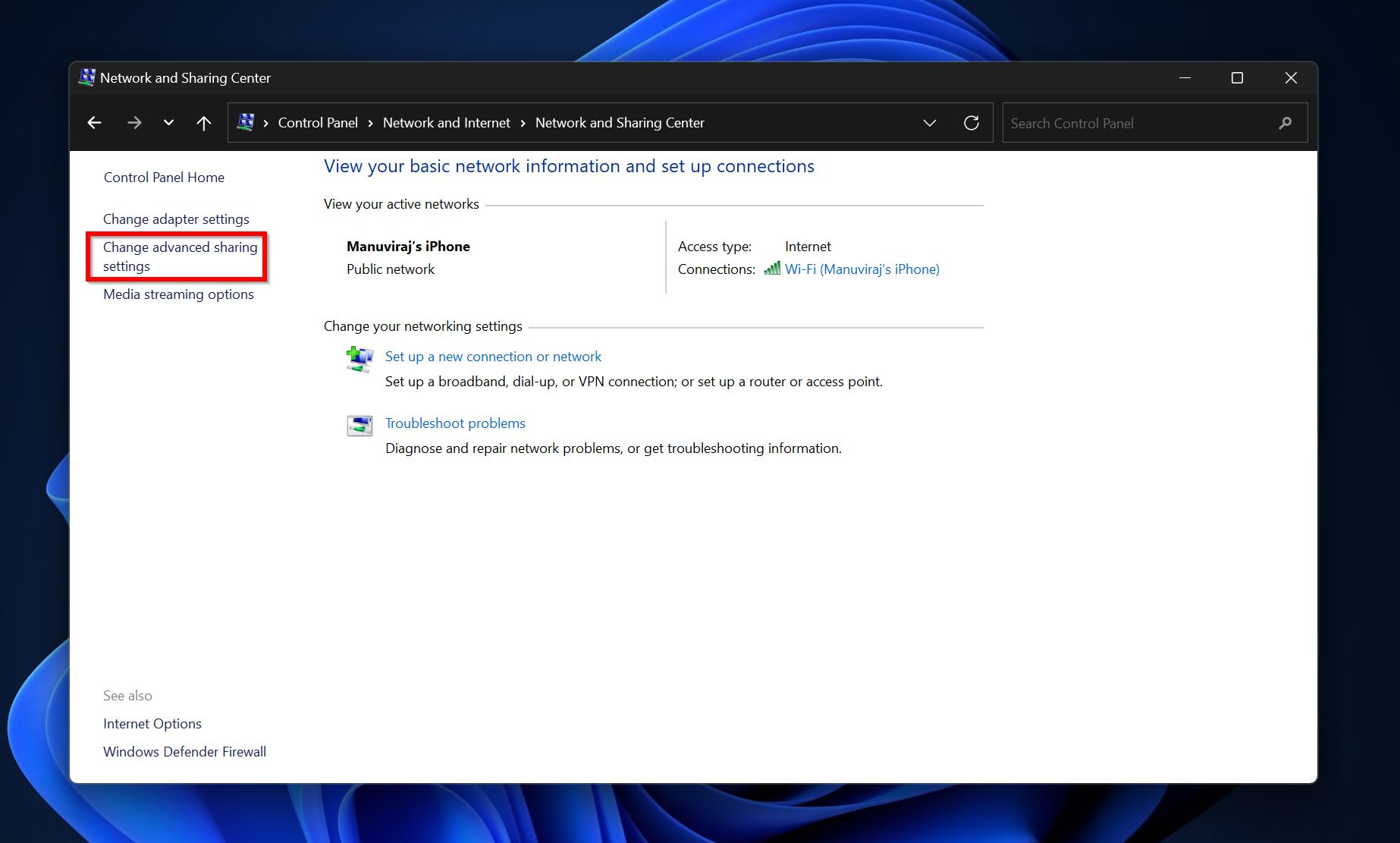
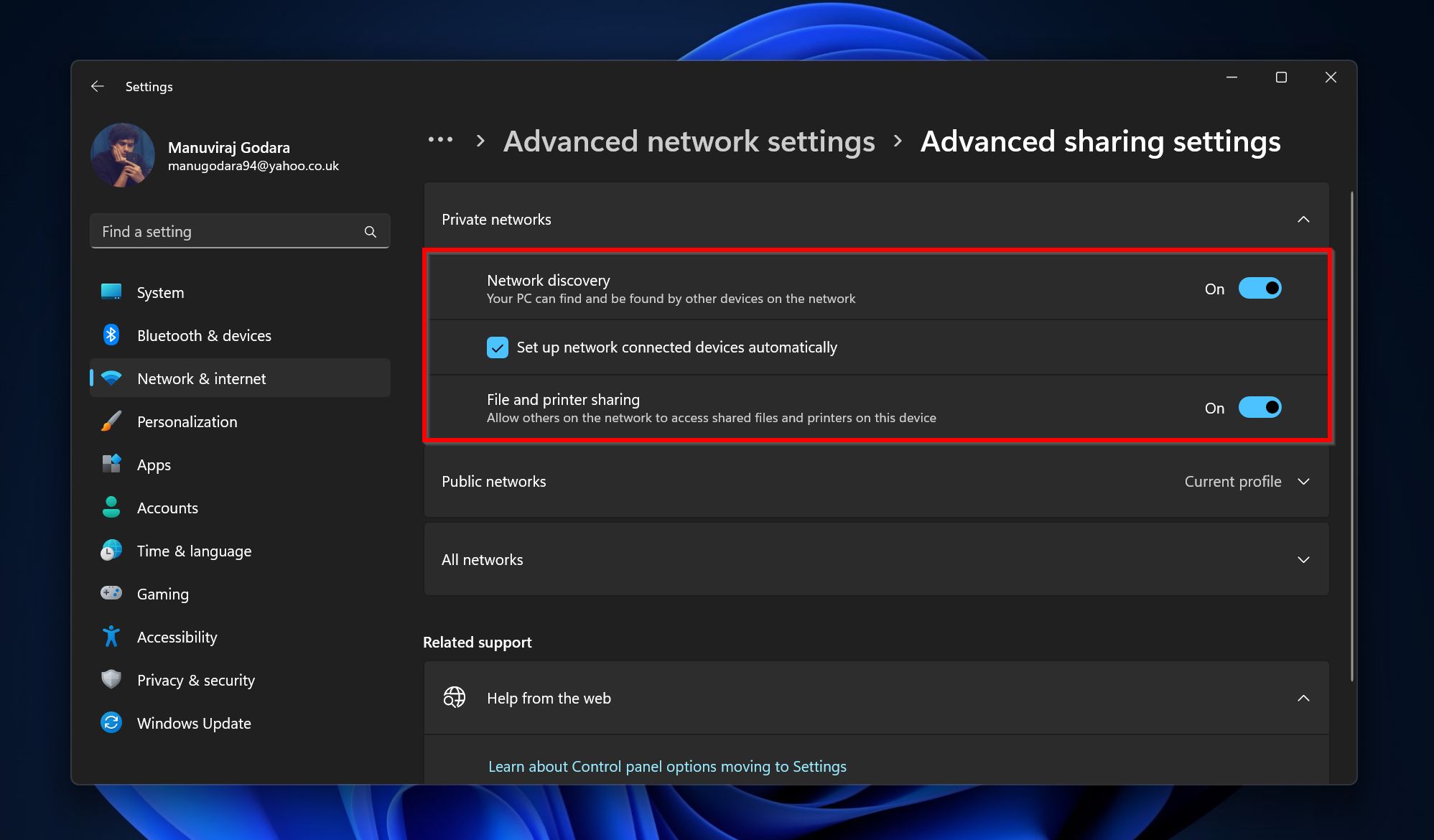
- Ensure that Network discovery, and File and printer sharing are switched on.
Method 8: Check if the Folder Is Encrypted
The Professional version of Windows allows users to encrypt folders. Encrypted folders can only be accessed by users who have the required key. If you’re logged in to a user account without the required key, you won’t be able to access the folder. It’s a good idea to check whether the folder is encrypted and log in using an account that has the required key.
Here’s how you can check if the folder and its contents are encrypted:
- Navigate to the folder in the File Explorer (Windows Key + E), and right-click on it, choose Properties.
- In the General tab, click on Advanced in the Attributes section.
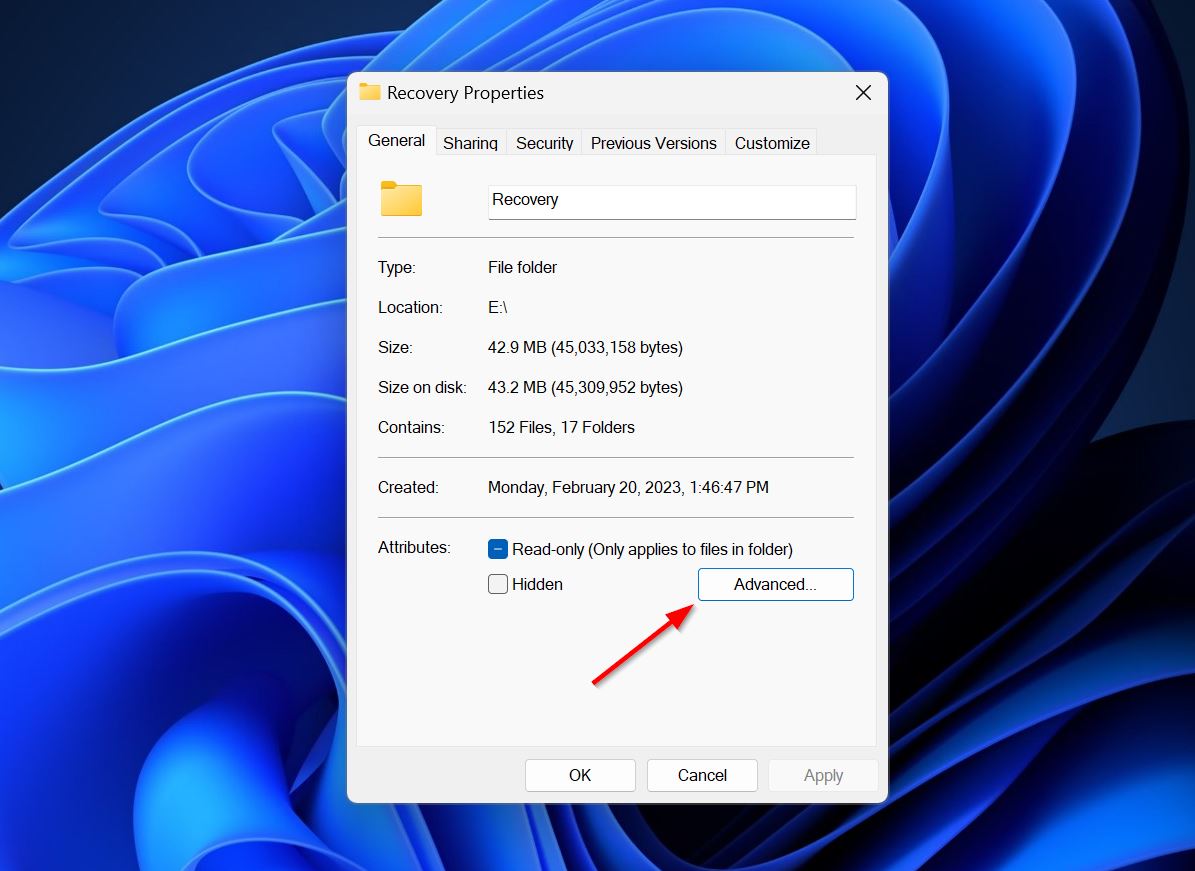
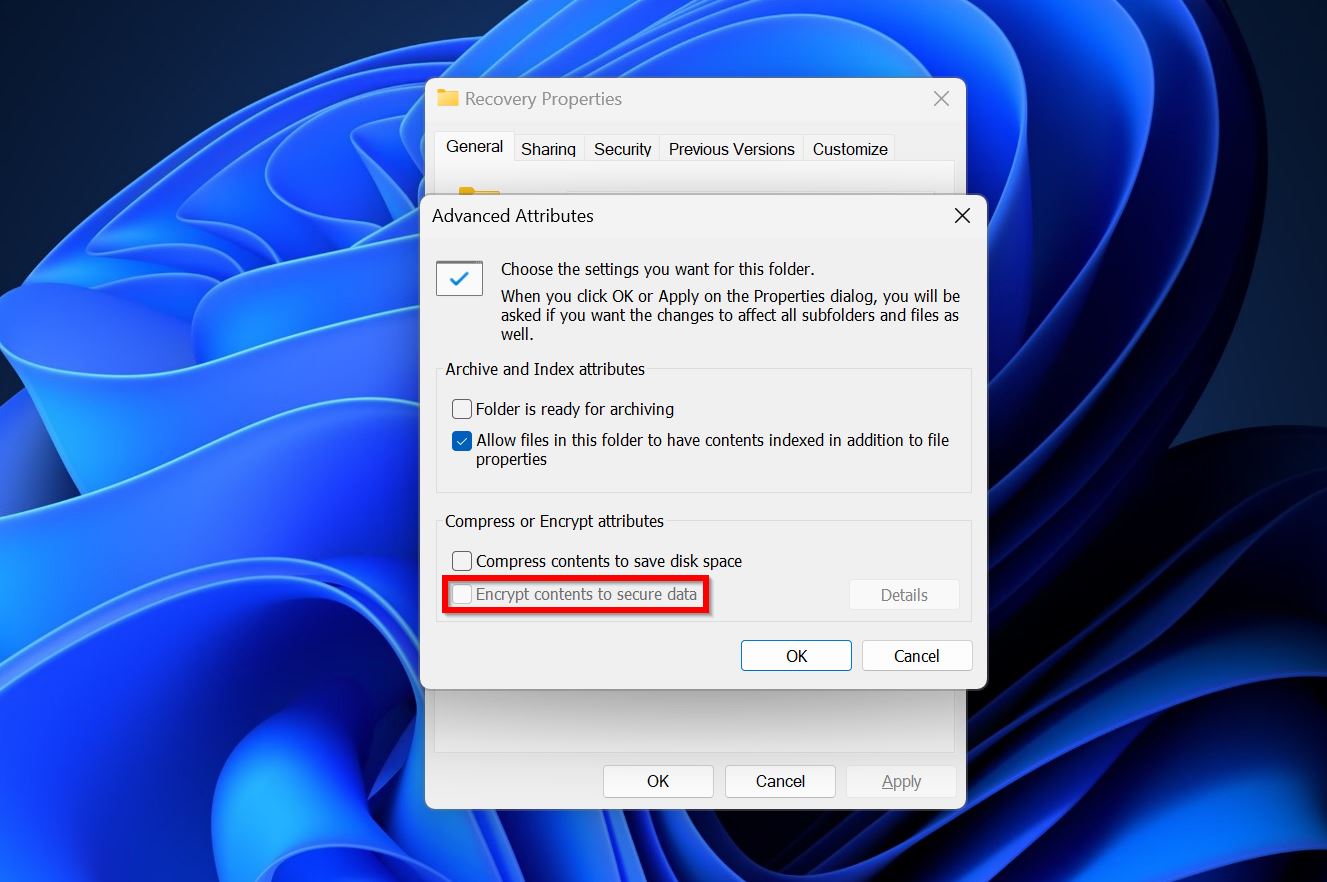
- See whether the Encrypt contents to secure data option is checked or not. If it’s checked, it means the folder is encrypted. You can also attempt to uncheck that box and see if it helps.
Method 9: Disable the User Account Control Prompt
The User Account Control (UAC) prompt can occasionally cause issues when you attempt to change the ownership of a folder. Fortunately, there’s a way around this – disable the UAC and re-attempt to change the ownership of the required folder.
Here’s how you can disable the UAC:
- Type “uac” in Windows Search (Windows Key + S), and click on the Change User Account Control settings option.
- Move the slider down to Never notify and click OK.
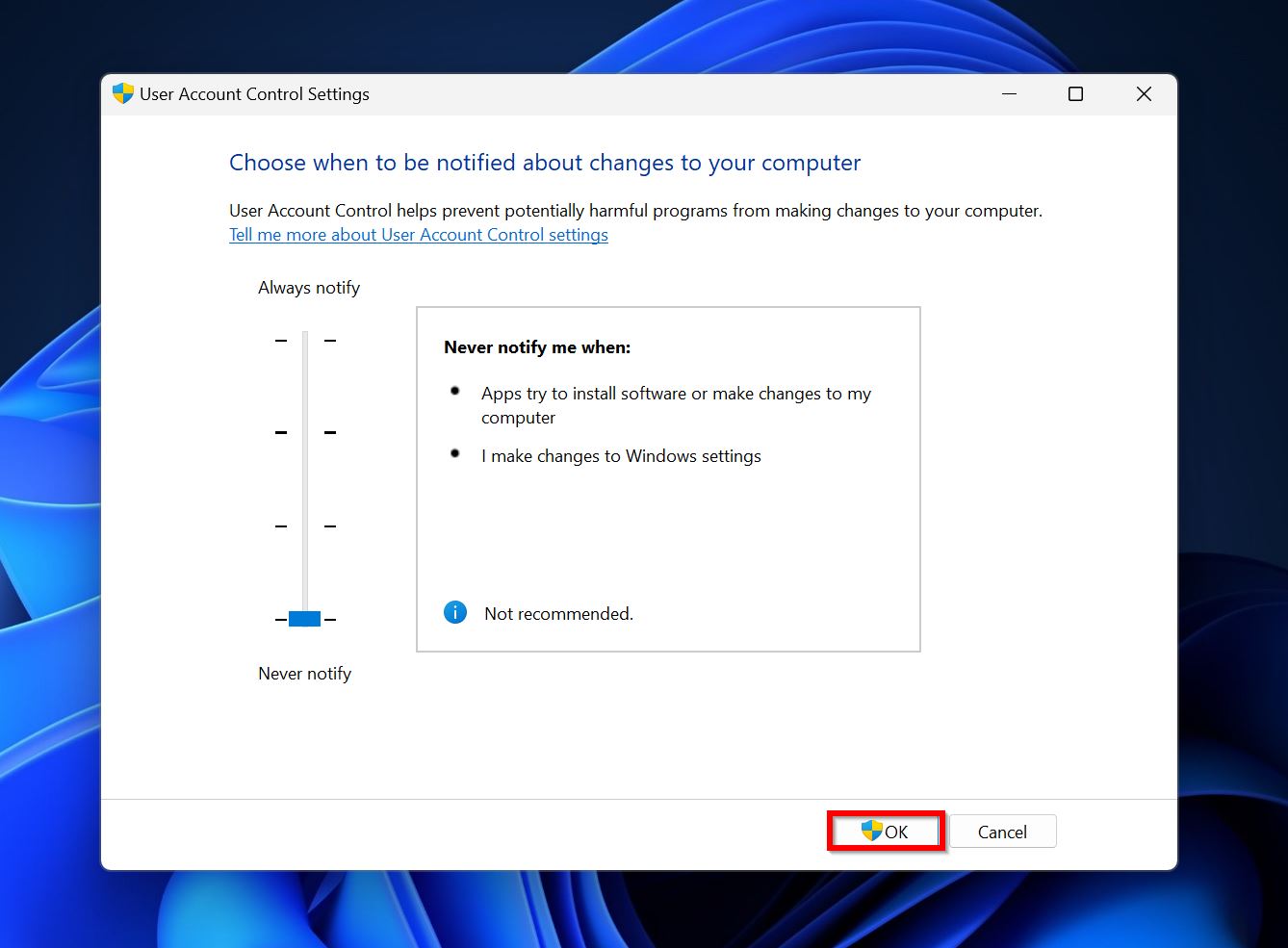
- Once you’re done changing the ownership, we recommend you move the slider back up to where it was, as this tool sometimes is the first line of defense from malware attacks
Method 10: Run CHKDSK
If none of the methods above were able to resolve the folder access denied error, bad sectors could be causing the issue. You can use an in-built Windows utility – CHKDSK, to scan the drive for bad sectors and repair it. Being a command-line utility, you need to use the Command Prompt (CMD) to run it.
Here’s how to use CHKDSK:
- Type “cmd” in Windows Search (Windows Key + S). In the search results, right-click on Command Prompt > Run as administrator.
- In the console, type chkdsk Y: /r /x and press Enter. Replace Y with the drive letter of the partition which contains the folder you can’t access.
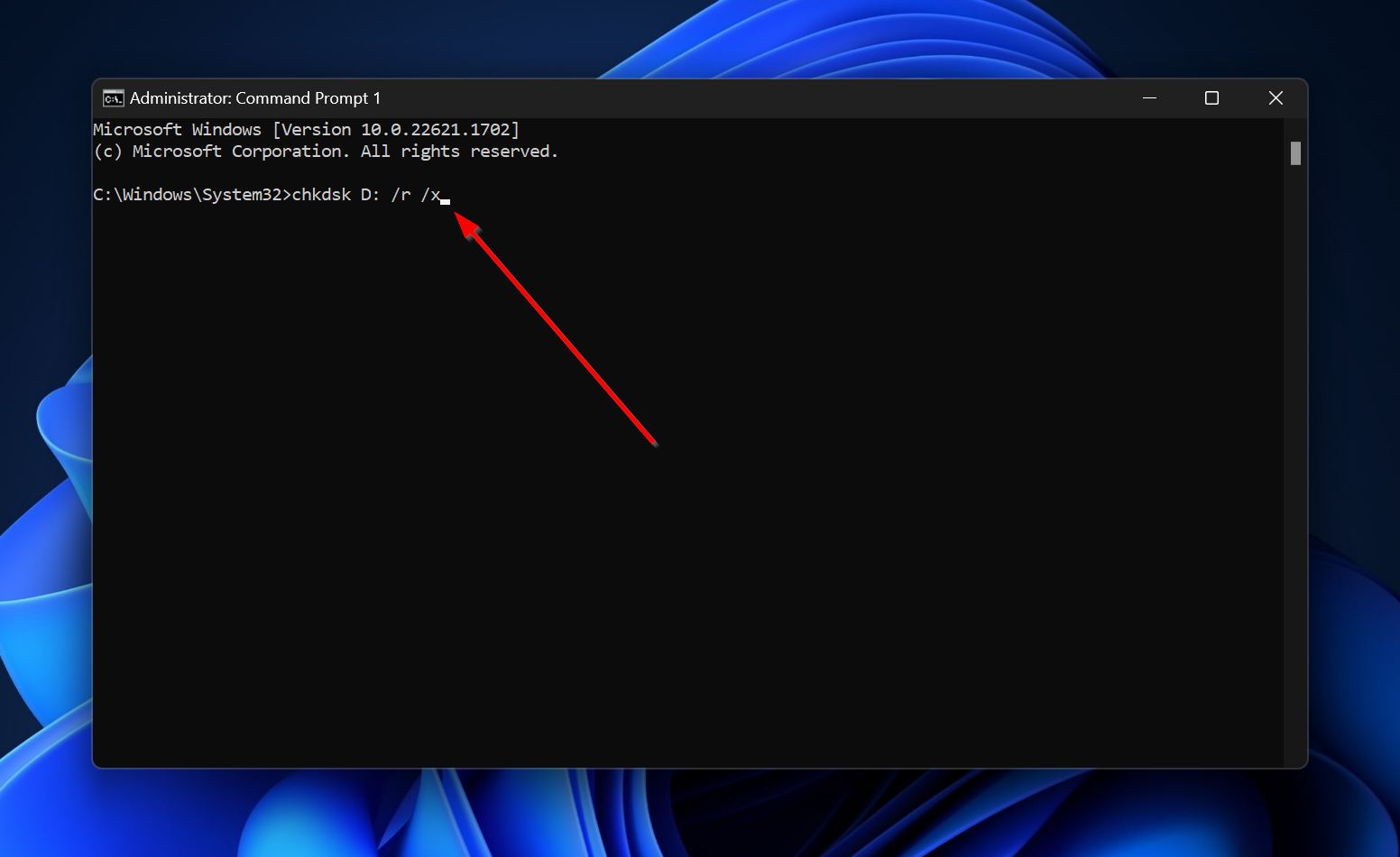
- Wait for CHKDSK to scan and repair the bad sectors, then reboot your PC.
Conclusion
Usually, the folder access denied error is nothing to be too worried about. A quick trip to the permission settings can resolve the issue. But, the chances of there being a serious reason behind the error are never zero. It’s best to regularly back up all your important data, preferably to the cloud as well as a local storage drive.
FAQ
- Ensure the folder is not in use by another program.
- Access the folder using an administrator account.
- Take ownership of the folder.
- Change the folder permissions.
- Check the antivirus settings.
- Turn on Network Discovery and File Sharing.
- Ensure the folder is not encrypted.
- Disable the User Account Control (UAC) prompt.
- Run CHKDSK to repair bad sectors.




