 “Will System Restore recover my deleted files?” Many of us have asked this question. This guide clears the air on whether System Restore recovers your files and what the feature’s purpose is. As a bonus, we’ve also included a user-friendly way to actually recover your deleted files.
“Will System Restore recover my deleted files?” Many of us have asked this question. This guide clears the air on whether System Restore recovers your files and what the feature’s purpose is. As a bonus, we’ve also included a user-friendly way to actually recover your deleted files.
Will a System Restore Recover Deleted Files?
No. System Restore will not recover any deleted personal files. This includes any photos, videos, documents, and music you may have saved in the user library folders and anywhere else on your PC. If you’re looking to bring back deleted personal files like your downloads or pictures, skip System Restore and follow our guide in the next section.
Windows System Restore’s primary purpose is to undo any problematic changes that were made to Windows. It takes a “snapshot” of the state of your PC at regular intervals (once in 7 days, by default, or earlier if changes are made to the PC), and when certain activities–like installing software, critical Windows updates, and updating or installing hardware drivers–take place.
❗ After running System Restore, you may observe that certain programs have been uninstalled, and others, reinstalled. In case a program is uninstalled, your personal files related to that app will remain unaffected. For example, System Restore could uninstall Adobe Premiere Pro, but your projects and video files in the Documents folder will remain untouched.
If you notice your PC has been acting strange, or you’re frequently running into errors, it’s a good idea to use System Restore:
- Type “system restore” in Windows Search. Click on Create a restore point from the search results.
- Click on the System Restore option in the next window.
- Click on Next in the System Restore welcome screen.
- Pick a Restore Point and click Next.
- Click on Finish to begin the System Restore process.
Two Ways to Recover Deleted Personal Files on Windows
The easiest way to recover permanently deleted files at home, is to use third-party data recovery programs. These tools can also recover deleted files that are not in the Recycle bin.
Keep the following tips in mind to maximize your chances of recovering all your files:
- Attempt data recovery as soon as possible.
- Avoid writing new files to the drive.
- Choose an option only from the best data recovery apps, right from the get-go, because the first data recovery scan is typically the most successful.
Method 1:Use a Professional Data Recovery Tool
Aside from contacting a professional data recovery service, professional data recovery tools are your best shot at restoring permanently deleted files, without a backup. There are plenty of such data recovery apps and you can take your pick.
For this tutorial, we opted to use Disk Drill, as it was the perfect fit. The program is easy to use, compatible with all major file systems and storage device types, and can detect over 400 file formats. It also has an in-built preview feature that lets you see exactly which file you’re recovering. You also get a free trial (for Windows users) that lets you recover up to 500 MB of data without paying a penny.
Here’s how you can recover deleted files using Disk Drill:
- Download Disk Drill and install it.
- Open Disk Drill, select the drive or partition you want to recover data from, and click Search for lost data.
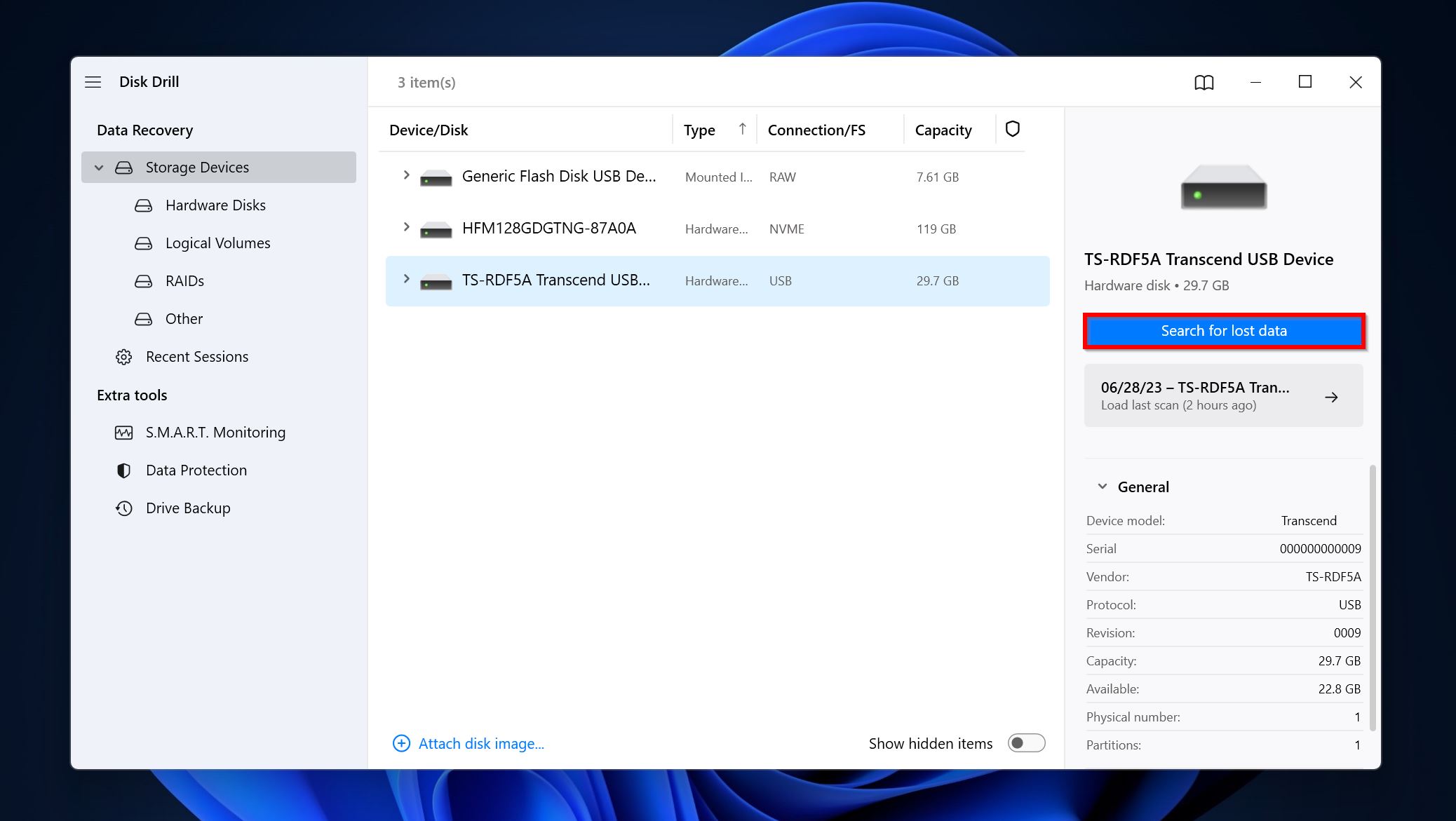
- Click on Review found items to view all the recoverable files Disk Drill has discovered. You can directly filter out the results by clicking on the required file type as well (Pictures, Video, Audio, Documents, Archives, and Other).
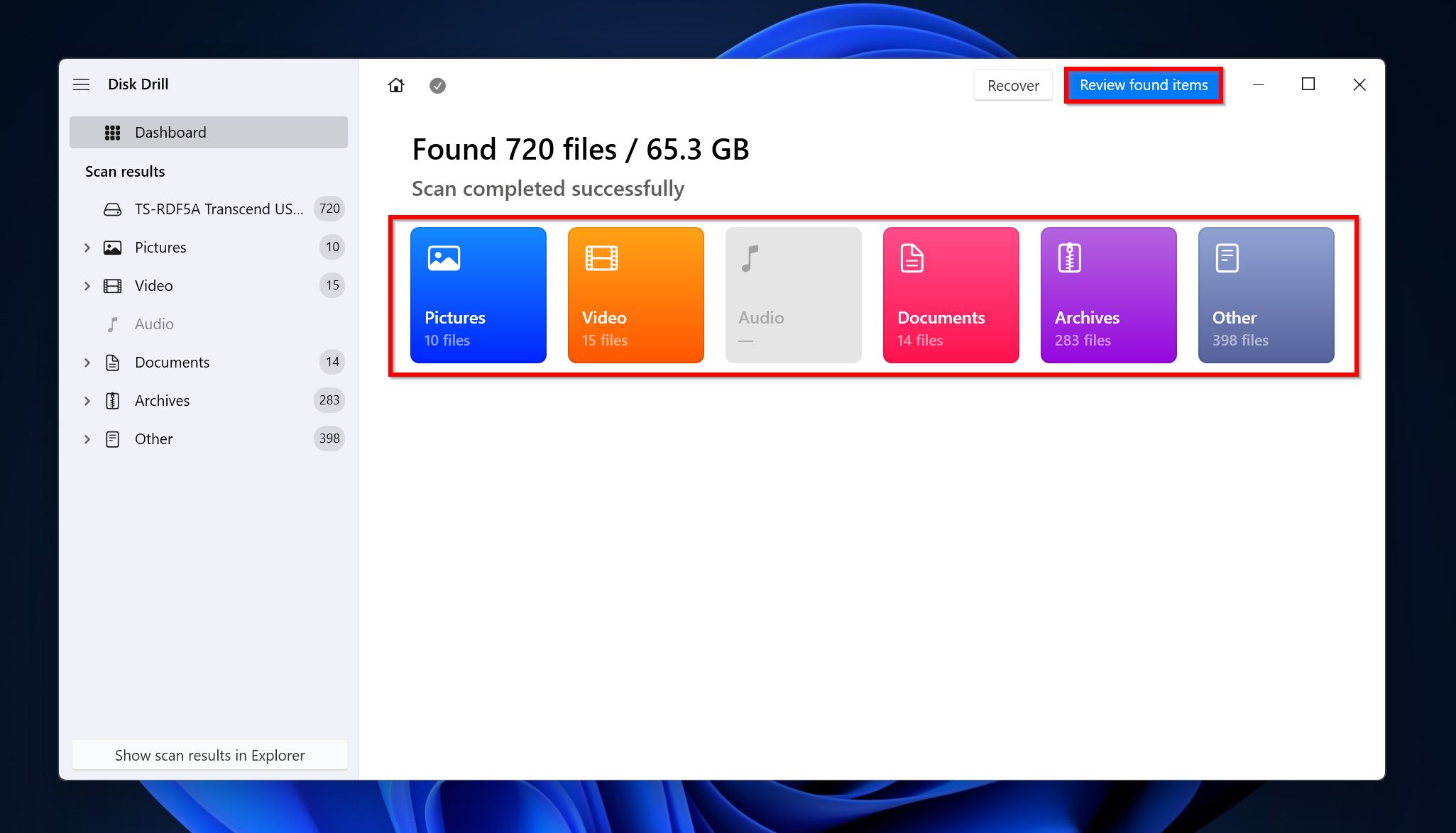
- Expand the Deleted or lost and Reconstructed sections to view deleted files. The Existing section will contain files that are already on the drive.
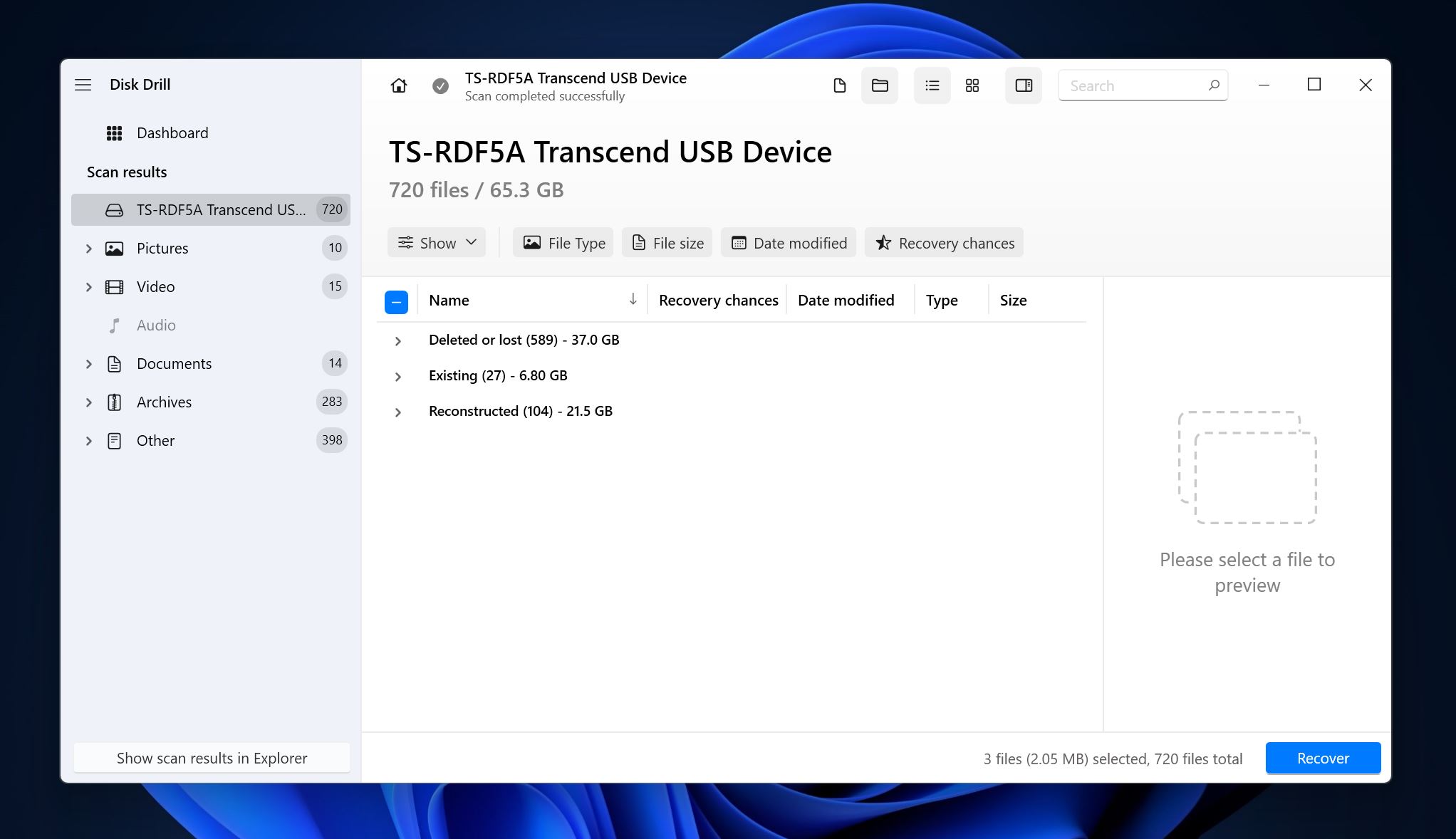
- Select the files you wish to recover. Disk Drill displays a preview of the currently selected file, but you can manually preview a file by clicking the eye icon next to its filename. Click on Recover once you’re done with your selection.
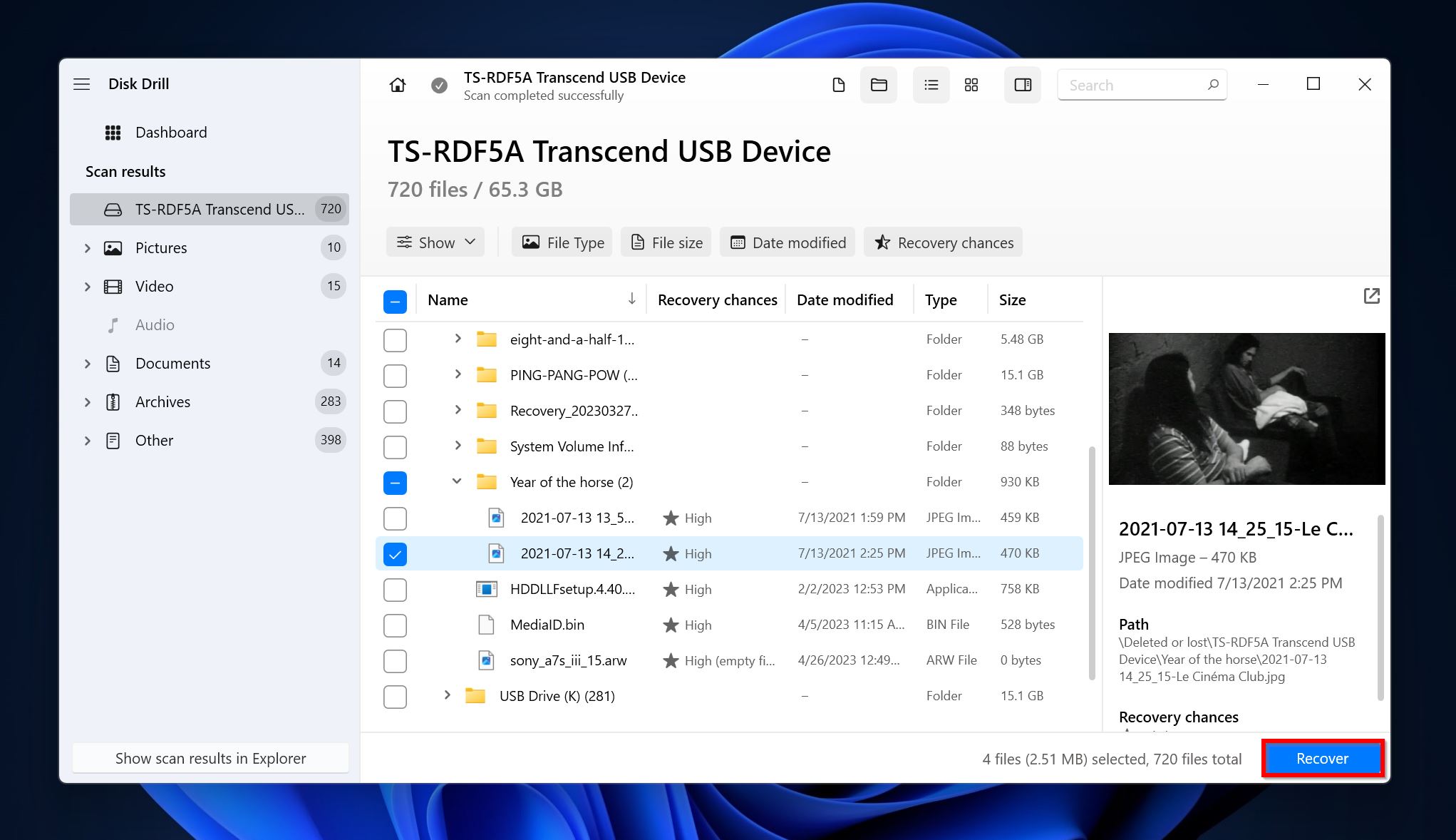
- Pick a recovery destination for your files and click Next. We recommend you recover these files to a separate drive.
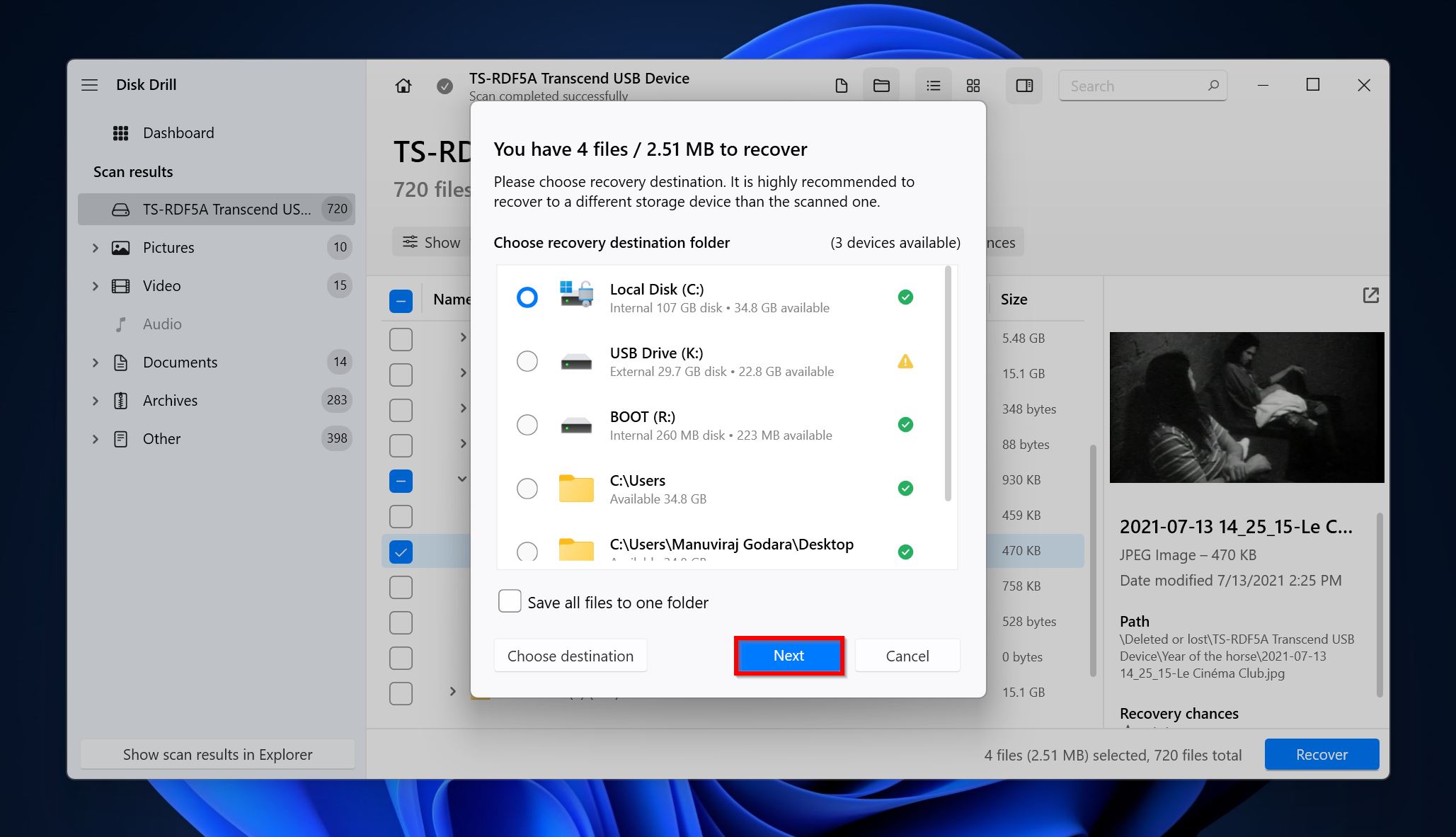
- Disk Drill will recover your files.
🎁 Bonus tip: If you forgot to recover some files in the first attempt, don’t worry, you won’t have to scan the drive again. Disk Drill automatically saves your scans–simply open the app and go to Recent sessions and choose the relevant saved scan.
Method 2:Use a Free Data Recovery Software
If the data you wish to recover isn’t that important, and you can’t justify spending money on its recovery, you can opt to use a freeware – Windows File Recovery. While it could help you recover some of your files, the program has several limitations. It can’t scan entire drives, only partitions, and has limited file system support.
Keep in mind that Windows File Recovery only works on Windows 10 (build 19041 onwards) and Windows 11.
Windows File Recovery is a command-line based tool, so ensure you follow the instructions below carefully:
- Download Windows File Recovery from the Microsoft Store.
- Launch the program.
- The basic syntax for data recovery is
winfr X: Y:RecoveryDestination /regular. Replace X and Y with the partition you want to recover data from and the place where wish to save the recovered files, respectively. You can add the/extensiveparameter instead of/regularif you wish to scan the partition thoroughly. Additionally, /regular only supports NTFS partitions.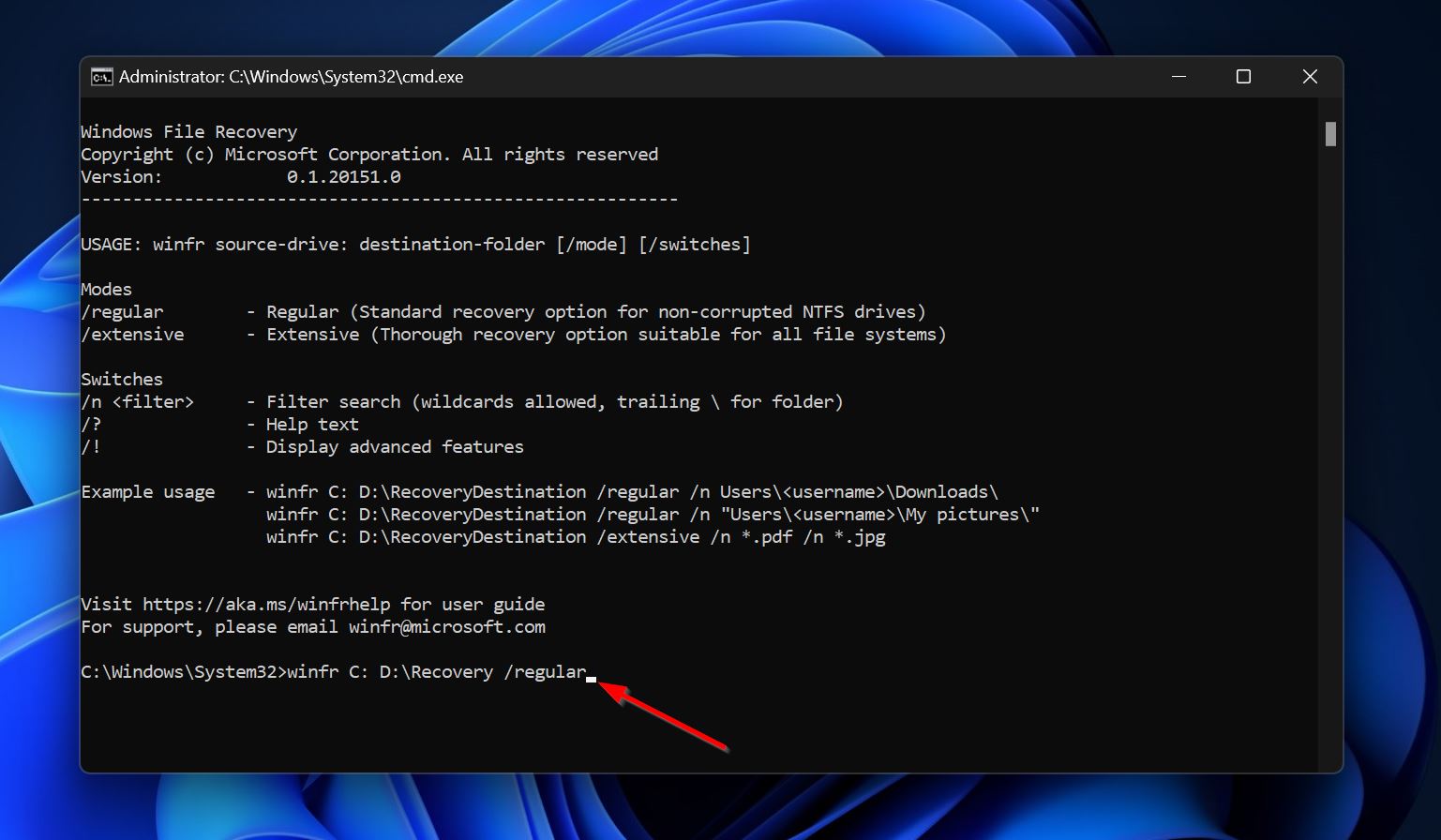
For more info about Windows File Recovery and its various recovery parameters, check out Microsoft’s support page for the tool.
Conclusion
System Restore is a useful feature that lets you hit the undo button on problematic software installations, Windows updates, and other Windows problems, without having to reinstall your OS. But if it’s personal files you’re looking to recover, you can either–get them back using data recovery apps, contact a professional data recovery service, or restore them from a backup.




